Python 官方文档:入门教程 => 点击学习
目录存储结构示意图初始化循环链表 循环链表的插入首位置代码实现其他位置代码实现(总)循环链表的删除1.操作的为第一个元素2.操作元素不为第一个元素代码实现(总)循环链表的常见操作

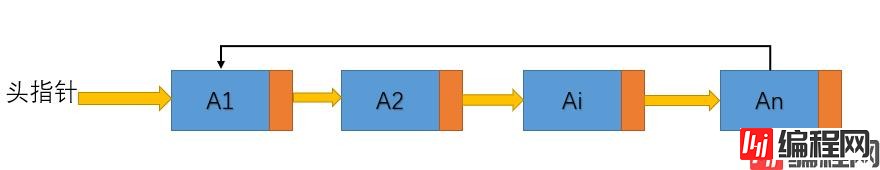
优点 : 能够通过任意结点遍历整个链表结构
1.循环链表的结点
typedef struct Circularnode {
ElementType date; //数据域
struct CircularNode* next; //指向下一个结点的指针域
}CircularNode;2.循环链表结构
typedef struct CircularLinkList {
CircularNode* next; //指向第一个结点的头指针,头指针
int length;
}CircularLinkList;需要考虑两种情况
1.插入的链表长度为 0 node -> next = node;
2.插入的链表长度不为0 node -> next = clList -> next lastNode -> next = node





void InsertCircularLinkList(CircularLinkList* clList, int pos, ElementType element)
{
//创建一个空节点
CircularLinkList* node = (CircularLinkList*)malloc(sizeof(CircularLinkList));
node->date = element;
node->next = NULL;
if (pos == 1) {
node->next = clList->next;
if (!node->next) {
//如果插入的链表长度为0
node->next = node;
}
else {
//如果长度不为0,就要找到链表的最后一个结点并改变其指针域
CircularLinkList* lastNode = clList->next;
for (int i = 1; i < clList->length; i++)
{
lastNode = lastNode->next;
}
clList->next = node;
clList->length++;
}
return;
}
//插入的不是第一个结点
CircularLinkList* currNode = clList->next;
for (int i = 1; i < pos - 1; i++)
currNode = currNode->next;
if (currNode) {
node->next = currNode->next;
currNode->next = node;
clList->length++;
if (pos == clList->length) {
node->next = clList->next;
}
}
}
代码实现


代码实现

ElementType DeleteCircularLinkList(CircularLinkList* clList, int pos)
{
ElementType element;
element.id = -999;
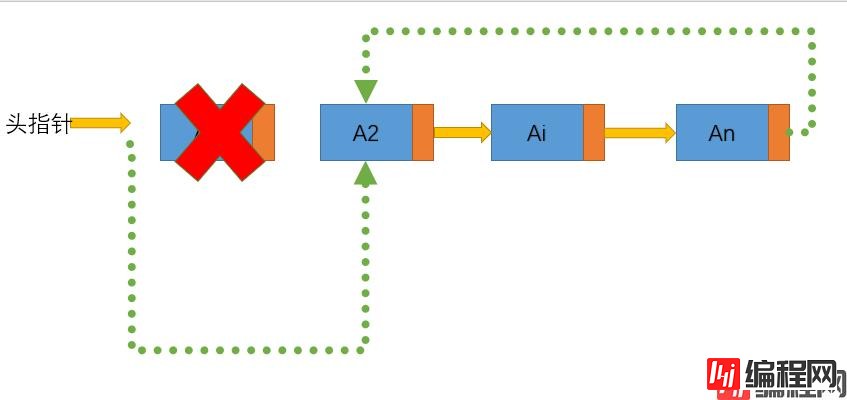
if (pos == 1) {
CircularLinkList* node = clList->next;
if (node) {
//找到最后一个结点,改变其指针域的指向
CircularLinkList* lastNode = clList->next;
for (int i = 1; i < clList->length; i++) {
lastNode = lastNode->next;
}
clList->next = node->next;
lastNode->next = clList->next;
free(node);
clList->length--;
}
return;
}
CircularLinkList* preNode;
CircularLinkList* node = clList->next;
for (int i = 1; node && i < pos; i++) {
preNode = node;
node = node->next;
}
if (node) {
element = node->date;
preNode->next = node->next;
free(node);
clList->length--;
}
return element;
}已知 P 结点是循环链表的中间结点,通过该节点遍历循环链表


代码实现
CircularNode* GetCircularLinkListNode(CircularLinkList* clList, ELementType element)
{
CircularNode* node = clList->next;
if (!node) return NULL;
do {
if (element.id == node->date.id && strcmp(element.name, node->date.name) == 0) {
return node;
}
} while (node == clList->next);
return NULL;
}以上就是Java数据结构与算法学习之循环链表的详细内容,更多关于Java数据结构 循环链表的资料请关注编程网其它相关文章!
--结束END--
本文标题: Java数据结构与算法学习之循环链表
本文链接: https://www.lsjlt.com/news/161025.html(转载时请注明来源链接)
有问题或投稿请发送至: 邮箱/279061341@qq.com QQ/279061341
下载Word文档到电脑,方便收藏和打印~
2024-03-01
2024-03-01
2024-03-01
2024-02-29
2024-02-29
2024-02-29
2024-02-29
2024-02-29
2024-02-29
2024-02-29
回答
回答
回答
回答
回答
回答
回答
回答
回答
回答
0