目录一、栈与队列以及双端队列的概念1.1 栈的概念及结构1.2 队列的概念及结构1.3 双端队列的概念及结构二、栈的实现和模拟栈2.1 实现一个支持动态增长的栈2.2 数组模拟静态栈
栈:一种特殊的线性表,其只允许在固定的一端进行插入和删除元素操作。进行数据插入和删除操作的一端 称为栈顶,另一端称为栈底。栈中的数据元素遵守后进先出LIFO(Last In First Out)的原则。
压栈:栈的插入操作叫做进栈/压栈/入栈,入数据在栈顶。
出栈:栈的删除操作叫做出栈。出数据也在栈顶

队列:只允许在一端进行插入数据操作,在另一端进行删除数据操作的特殊线性表,队列具有先进先出 FIFO(First In First Out)
入队列:进行插入操作的一端称为队尾
出队列:进行删除操作的一端称为队头

双端队列:是一种线性表,又称为双向队列,所有的插入和删除(通常还有所有的访问)都在表的两端进行。

栈的实现一般可以使用数组或者链表实现,相对而言数组的结构实现更优一些。因为数组在尾上插入数据的 代价比较小。、


头文件:
#pragma once
#include<stdio.h>
#include<stdlib.h>
#include<stdbool.h>
#include<assert.h>
typedef int STDataType;
typedef struct Stack//动态栈
{
int *a;
int top;//栈顶的位置
int capacity;//容量
}ST;
STDataType StackTop(ST* ps);//返回栈顶的值
void StackInit(ST* ps);//初始化栈
void StackDestory(ST* ps);//销毁栈
void StackPop(ST* ps);//弹出
void StackPush(ST* ps, STDataType x);//插入
bool StackEmpty(ST* ps);//判断栈是否为空。源文件:
#include"Stack.h"
void StackInit(ST* ps)//栈的初始化
{
assert(ps);
ps->a = NULL;//a点的值指向空
ps->top = 0;//栈底为0
ps->capacity = 0;//空间为0
}
void StackDestory(ST* ps)
{
assert(ps);
free(ps->a);//把a释放掉
ps->a = NULL;
ps->capacity = ps->top = 0;
}
void StackPush(ST* ps, STDataType x)//入数据
{
assert(ps);
//满了就扩容
if (ps->top == ps->capacity)//如果栈的栈顶恰好和容量相等就扩容
{
int newCapacity = ps->capacity == 0 ? 4 : ps->capacity * 2;
ps->a = (STDataType*)realloc(ps->a, newCapacity * sizeof(STDataType));
if (ps->a == NULL)
{
printf("realloc fail\n");
exit(-1);
}
ps->capacity = newCapacity;//新的空间赋给旧的
}
ps->a[ps->top] = x;//栈顶插入x;
ps->top++;//top++
}
void StackPop(ST* ps)
{
assert(ps);
assert(ps->top > 0);
--ps->top;//top--就相当于删除操作
}
bool StackEmpty(ST* ps)
{
assert(ps);
//两种写法
//if (ps->top > 0)
//{
// return false;
//}
//else
//{
// return true;
//}
return ps->top == 0;
}
STDataType StackTop(ST* ps)
{
assert(ps);
assert(ps->top > 0);
return ps->a[ps->top - 1];//访问栈顶元素(这里因为top我们设为0,所以访问栈顶元素相当于top-1
}
int StackSize(ST* ps)
{
assert(ps);
return ps->top;
}
#include<iOStream>
using namespace std;
const int N = 1e6 + 10;
int n;
int stk[N];
int top = - 1;
int main ()
{
cin >> n;
while(n --)
{
string s;
cin >> s;
if(s == "push")
{
int a;
cin >> a;
stk[++top] = a;
}
if(s == "pop")
{
top--;
}
if(s == "empty")
{
if(top >= 0) printf("NO\n");
else printf("YES\n");
}
if(s == "query")
{
printf("%d\n", stk[top]);
}
}
return 0;
}队列也可以数组和链表的结构实现,使用链表的结构实现更优一些,因为如果使用数组的结构,出队列在数 组头上出数据,效率会比较低。
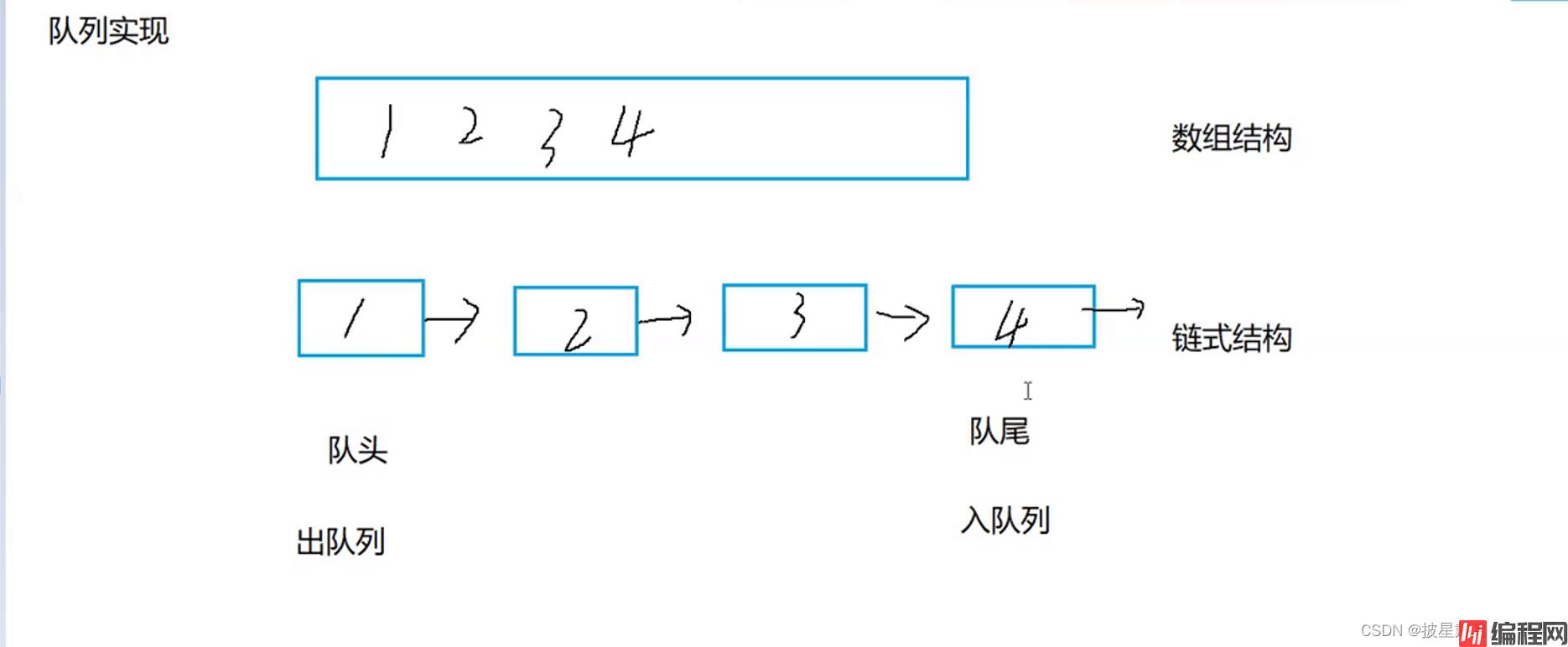
头文件:
#pragma once
#include<stdio.h>
#include<stdlib.h>
#include<stdbool.h>
#include<assert.h>
typedef int QDataType;//方便改类型
typedef struct Queuenode//保存每个节点的数据
{
QDataType data;
struct QueueNode* next;
}QNode;
typedef struct Queue
{
QNode* head;
QNode* tail;
}Queue;
//上面的写法等价于:
//typedef struct Queue
//{
// QNode* head;
// QNode* tail;
//};
//
//typedef struct Queue Queue;//
//一般实际情况哨兵位的头节点不存储值,不放数据
void QueueInit(Queue* pq);//队列初始化
void QueueDestory(Queue* pq);//队列销毁
void QueuePush(Queue* pq, QDataType x);//队尾插入
void QueuePop(Queue* pq);//弹出队头
bool QueueEmpty(Queue* pq);//判断是否为空
size_t QueueSize(Queue* pq);//size_t相当于Unsinged int
QDataType QueueFront(Queue* pq);
QDataType QueueBack(Queue* pq);源文件:
#include"Queue.h"
void QueueInit(Queue* pq)
{
assert(pq);
pq->head = pq->tail = NULL;
}
void QueueDestory(Queue* pq)
{
assert(pq);
QNode* cur = pq->head;
while (cur)
{
QNode* next = cur->next;//先记录下一个位置
free(cur);//free掉cur指针
cur = next;//cur赋值到下一个位置
}
pq->head = pq->tail = NULL;//置空
}
void QueuePush(Queue* pq, QDataType x)//队尾插入//插入int类型的参数
{
assert(pq);
QNode* newnode = (QNode*)malloc(sizeof(QNode));
assert(newnode);
newnode->data = x;//新的节点的值被赋与x
newnode->next = NULL;//新的节点是在队尾,所以指向的下一个位置是空
if (pq->tail == NULL)//如果链表的第一个值为空,则head = tail = NULL
{
assert(pq->head == NULL);
pq->head = pq->tail = newnode;
}
else//尾插
{
pq->tail->next = newnode;//先改指向
pq->tail = newnode;//再改地址
}
}
void QueuePop(Queue* pq)//弹出队首
{
assert(pq);
assert(pq->head && pq->tail);
if (pq->head->next == NULL)//只有一个节点
{
free(pq->head);
pq->head = pq->tail = NULL;
}
else
{
QNode* next = pq->head->next;//QNode* next相当于是QDataType的头指针的下一个位置
free(pq->head);
pq->head = next;//头往后走
}
}
bool QueueEmpty(Queue* pq)
{
assert(pq);
//return pq->head == NULL && pq->tail == NULL;
return pq->head == NULL;//程序调试了快一个小时就是因为pq->head没加后面的== NULL
}
size_t QueueSize(Queue* pq)//size_t相当于Unsinged int
{
assert(pq);
QNode* cur = pq->head;
size_t size = 0;
while (cur)
{
size++;
cur = cur->next;
}
return size;
}
QDataType QueueFront(Queue* pq)//返回队头第一个位的值
{
assert(pq);
assert(pq->head);
return pq->head->data;
}
QDataType QueueBack(Queue* pq)//返回队尾的值
{
assert(pq);
assert(pq->tail);
return pq->tail->data;
}
#include<iostream>
#include<cstring>
#include<alGorithm>
using namespace std;
const int N = 1e5 + 10;
int q[N];
int n;
int hh ,tt = -1;//hh表示头,tt表示尾
int main ()
{
cin >> n;
while(n --)
{
string s;
cin >> s;
if(s == "push")
{
int x;
cin >> x;
q[++tt] = x;
}
else if(s == "pop")
{
hh ++;
}
else if(s == "empty")
{
if(hh <= tt) printf("NO\n");//尾在逻辑上要比头更前面
else printf("YES\n");
}
else cout << q[hh] << endl;
}
return 0;
}225. 用队列实现栈 - 力扣(LeetCode)

代码:
typedef int QDataType;
typedef struct QueueNode//保存每个节点的数据
{
QDataType data;
struct QueueNode* next;
}QNode;
typedef struct Queue
{
QNode* head;
QNode* tail;
}Queue;
void QueueInit(Queue* pq);
void QueueDestory(Queue* pq);
void QueuePush(Queue* pq, QDataType x);//队尾插入
void QueuePop(Queue* pq);
bool QueueEmpty(Queue* pq);
size_t QueueSize(Queue* pq);//size_t相当于Unsinged int
QDataType QueueFront(Queue* pq);
QDataType QueueBack(Queue* pq);
void QueueInit(Queue* pq)
{
assert(pq);
pq->head = pq->tail = NULL;
}
void QueueDestory(Queue* pq)
{
assert(pq);
QNode* cur = pq->head;
while (cur)
{
QNode* next = cur->next;//先记录下一个位置
free(cur);//free掉cur指针
cur = next;//cur赋值到下一个位置
}
pq->head = pq->tail = NULL;//置空
}
void QueuePush(Queue* pq, QDataType x)//队尾插入
{
assert(pq);
QNode* newnode = (QNode*)malloc(sizeof(QNode));
assert(newnode);
newnode->data = x;
newnode->next = NULL;
if (pq->tail == NULL)//如果链表的第一个值为空,则head = tail = NULL
{
assert(pq->head == NULL);
pq->head = pq->tail = newnode;
}
else//尾插
{
pq->tail->next = newnode;
pq->tail = newnode;
}
}
void QueuePop(Queue* pq)//弹出队首
{
assert(pq);
assert(pq->head && pq->tail);
if (pq->head->next == NULL)//只有一个节点
{
free(pq->head);
pq->head = pq->tail = NULL;
}
else
{
QNode* next = pq->head->next;//QNode* next相当于是QDataType的头指针的下一个位置
free(pq->head);
pq->head = next;//头往后走
}
}
bool QueueEmpty(Queue* pq)
{
assert(pq);
//return pq->head == NULL && pq->tail == NULL;
return pq->head == NULL;//程序调试了快一个小时就是因为pq->head没加后面的== NULL
}
size_t QueueSize(Queue* pq)//size_t相当于Unsinged int
{
assert(pq);
QNode* cur = pq->head;
size_t size = 0;
while (cur)
{
size++;
cur = cur->next;
}
return size;
}
QDataType QueueFront(Queue* pq)//返回队头第一个位的值
{
assert(pq);
assert(pq->head);
return pq->head->data;
}
QDataType QueueBack(Queue* pq)
{
assert(pq);
assert(pq->tail);
return pq->tail->data;
}
typedef struct {
Queue q1;
Queue q2;
} MyStack;
MyStack* myStackCreate() {
MyStack* pst = (MyStack*)malloc(sizeof(MyStack));
assert(pst);
QueueInit(&pst->q1);
QueueInit(&pst->q2);
return pst;
}
void myStackPush(MyStack* obj, int x) {
assert(obj);
if(!QueueEmpty(&obj->q1))
{
QueuePush(&obj->q1, x);
}
else
{
QueuePush(&obj->q2, x);
}
}
int myStackPop(MyStack* obj) {
Queue* emptyQ = &obj->q1;//假设q1为空,q2不为空
Queue* nonEmptyQ = &obj->q2;
if(!QueueEmpty(&obj->q1))
{
emptyQ = &obj->q2;
nonEmptyQ = &obj->q1;
}
//把非空队列的前N个数据导入空队列,剩下一个删掉
//就实现了后进先出
while(QueueSize(nonEmptyQ) > 1)
{
QueuePush(emptyQ, QueueFront(nonEmptyQ));
QueuePop(nonEmptyQ);
}
int top = QueueFront(nonEmptyQ);//此时那个非空的队列只剩下一个数据
QueuePop(nonEmptyQ);
return top;
}
int myStackTop(MyStack* obj) {
assert(obj);
if(!QueueEmpty(&obj->q1))//如果q1不为空
{
return QueueBack(&obj->q1);
}
else
{
return QueueBack(&obj->q2);
}
}
bool myStackEmpty(MyStack* obj) {
return QueueEmpty(&obj->q1) && QueueEmpty(&obj->q2);
}
void myStackFree(MyStack* obj) {
assert(obj);
QueueDestory(&obj->q1);
QueueDestory(&obj->q2);
free(obj);
}232. 用栈实现队列 - 力扣(LeetCode)栈是后进先出
思路:设计两个栈,一个栈专门用来入数据,一个栈专门用来出数据。

typedef int STDataType;
typedef struct Stack//动态链表
{
int *a;
int top;//栈顶的位置
int capacity;//容量
}ST;
STDataType StackTop(ST* ps);
void StackInit(ST* ps);//初始化栈
void StackDestory(ST* ps);
void StackPop(ST* ps);
void StackPush(ST* ps, STDataType x);
bool StackEmpty(ST* ps);
void StackInit(ST* ps)
{
assert(ps);
ps->a = NULL;
ps->top = 0;
ps->capacity = 0;
}
void StackDestory(ST* ps)
{
assert(ps);
free(ps->a);
ps->a = NULL;
ps->capacity = ps->top = 0;
}
void StackPush(ST* ps, STDataType x)//入数据
{
assert(ps);
//满了就扩容
if (ps->top == ps->capacity)
{
int newCapacity = ps->capacity == 0 ? 4 : ps->capacity * 2;
ps->a = (STDataType*)realloc(ps->a, newCapacity * sizeof(STDataType));
if (ps->a == NULL)
{
printf("realloc fail\n");
exit(-1);
}
ps->capacity = newCapacity;
}
ps->a[ps->top] = x;
ps->top++;
}
void StackPop(ST* ps)
{
assert(ps);
assert(ps->top > 0);
--ps->top;
}
bool StackEmpty(ST* ps)
{
assert(ps);
//两种写法
//if (ps->top > 0)
//{
// return false;
//}
//else
//{
// return true;
//}
return ps->top == 0;
}
STDataType StackTop(ST* ps)
{
assert(ps);
assert(ps->top > 0);
return ps->a[ps->top - 1];//访问栈顶元素
}
int StackSize(ST* ps)
{
assert(ps);
return ps->top;
}
typedef struct
{
ST pushST;
ST popST;
} MyQueue;
MyQueue* myQueueCreate() {
MyQueue* obj = (MyQueue*)malloc(sizeof(MyQueue));
assert(obj);
StackInit(&obj->pushST);//&符要加,要改变结构体里面的内容
StackInit(&obj->popST);
return obj;
}
void myQueuePush(MyQueue* obj, int x) {
assert(obj);
StackPush(&obj->pushST, x);
}
int myQueuePop(MyQueue* obj) {
assert(obj);
//如果popST为空, 把pushST的数据拿过来,就符合先进先出的顺序了
if(StackEmpty(&obj->popST))//如果ST Pop为空就执行
{
while(!StackEmpty(&obj->pushST))
{
StackPush(&obj->popST, StackTop(&obj->pushST));
StackPop(&obj->pushST);//把pushST里的数据删掉
}
}
int front = StackTop(&obj->popST);//记录栈顶的数据
StackPop(&obj->popST);
return front;
}
int myQueuePeek(MyQueue* obj) {
assert(obj);
//如果popST为空, 把pushST的数据拿过来,就符合先进先出的顺序了
if(StackEmpty(&obj->popST))//如果ST Pop为空就执行
{
while(!StackEmpty(&obj->pushST))
{
StackPush(&obj->popST, StackTop(&obj->pushST));
StackPop(&obj->pushST);//把pushST里的数据删掉
}
}
return StackTop(&obj->popST);
}
bool myQueueEmpty(MyQueue* obj) {
assert(obj);
return StackEmpty(&obj->pushST)&&StackEmpty(&obj->popST);
}
void myQueueFree(MyQueue* obj) {
assert(obj);
StackDestory(&obj->pushST);
StackDestory(&obj->popST);
free(obj);
}本文分别从(1)栈、队列以及双端队列的概念、(2)栈的实现(动态)和模拟静态栈、(3)队列的实现(动态)和模拟静态队列、(4)leetcode-栈实现队列和用队列实现栈四个方面对栈和队列这两个数据结构进行了分析,希望大家读后能够有所收获,也希望大家多多支持。
到此这篇关于C语言近万字为你讲透栈和队列的文章就介绍到这了,更多相关C语言栈和队列内容请搜索编程网以前的文章或继续浏览下面的相关文章希望大家以后多多支持编程网!
--结束END--
本文标题: C语言近万字为你讲透栈和队列
本文链接: https://www.lsjlt.com/news/149791.html(转载时请注明来源链接)
有问题或投稿请发送至: 邮箱/279061341@qq.com QQ/279061341
下载Word文档到电脑,方便收藏和打印~
2024-03-01
2024-03-01
2024-02-29
2024-02-29
2024-02-29
2024-02-29
2024-02-29
2024-02-29
2024-02-29
2024-02-29
回答
回答
回答
回答
回答
回答
回答
回答
回答
回答
0