Python 官方文档:入门教程 => 点击学习
简述 我们在工作中会碰到需要使用带过期时间的缓存场景。但是使用Redis有太重了,毕竟缓存的数据很小,放在内存够够的。hutools提供了TimedCache时间缓存工具,可以实现该
我们在工作中会碰到需要使用带过期时间的缓存场景。但是使用Redis有太重了,毕竟缓存的数据很小,放在内存够够的。hutools提供了TimedCache时间缓存工具,可以实现该场景。下面使用到该组件,并为了适配工作场景,对该工具类做优化升级。
<dependency>
<groupId>cn.hutool</groupId>
<artifactId>hutool-all</artifactId>
<version>5.4.6</version>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>com.Google.guava</groupId>
<artifactId>guava</artifactId>
<version>30.1.1-jre</version>
</dependency>不多说了,上代码。
import cn.hutool.cache.CacheUtil;
import cn.hutool.cache.impl.TimedCache;
import cn.hutool.core.thread.ThreadUtil;
public class TimedCacheUtils {
private static final TimedCache<String, String> TIMED_CACHE = CacheUtil.newTimedCache(5000);
static {
TIMED_CACHE.schedulePrune(5);
}
public static void put(String key, String value, Long timeout) {
TIMED_CACHE.put(key, value, timeout);
}
public static String get(String key) {
return TIMED_CACHE.get(key);
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
put("haha", "1", 3000L);
ThreadUtil.sleep(2000);
// if (TIMED_CACHE.containsKey("haha")) {
// System.out.println("aa");
// }
System.out.println("第1次结果:" + get("haha"));
ThreadUtil.sleep(2000);
System.out.println("第2次结果:" + get("haha"));
ThreadUtil.sleep(5000);
System.out.println("第3次结果:" + get("haha"));
// 取消定时清理
TIMED_CACHE.cancelPruneSchedule();
}
}首先我们看一下执行的效果
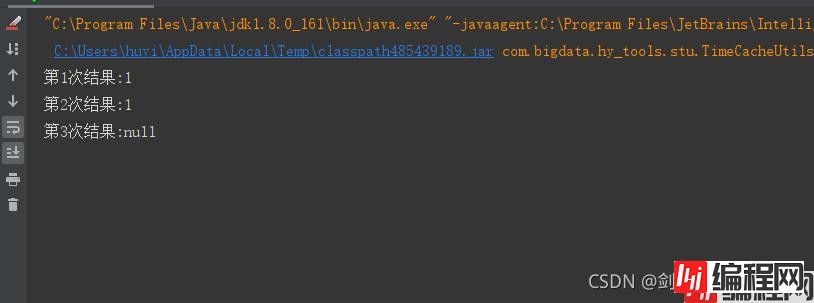
说明:
1、设置的超时时间为3000毫秒,所以第一次打印在2秒钟,所以可以获取到值。
2、因为第一次打印调用了get方法,刷新了过期时间,所以依然可以获取到值。
3、第三次打印在5秒后,所以已经过期,无法获取到值,打印null。
那么,需要知道是否缓存还在可以使用containsKey方法。如下:
put("haha", "1", 3000L);
ThreadUtil.sleep(2000);
if (TIMED_CACHE.containsKey("haha")) {
System.out.println("第1次结果:缓存存在");
}
// System.out.println("第1次结果:" + get("haha"));
ThreadUtil.sleep(2000);
System.out.println("第2次结果:" + get("haha"));
ThreadUtil.sleep(5000);
System.out.println("第3次结果:" + get("haha"));
// 取消定时清理
TIMED_CACHE.cancelPruneSchedule();执行结果如下:
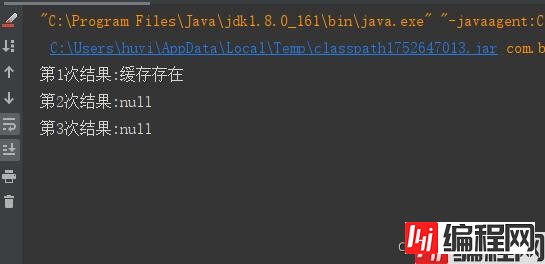
我们在使用TimedCache会发现,一旦缓存过期我们并不能立马知道,很多工作场景中需要对缓存做监听回调。所以我升级了一下该工具类。
import cn.hutool.cache.CacheUtil;
import cn.hutool.cache.impl.TimedCache;
import cn.hutool.core.thread.ThreadUtil;
import com.google.common.util.concurrent.*;
import org.checkerframework.checker.nullness.qual.Nullable;
import java.text.MessageFORMat;
import java.util.concurrent.ConcurrentHashMap;
import java.util.concurrent.ExecutorService;
import java.util.concurrent.Executors;
import java.util.function.Consumer;
public class TimedCacheUtils {
private static final TimedCache<String, String> TIMED_CACHE = CacheUtil.newTimedCache(5000);
private static final ExecutorService executorService = Executors.newCachedThreadPool();
private static final ListeningExecutorService listeningExecutorService =
MoreExecutors.listeningDecorator(executorService);
private static ConcurrentHashMap<String, Consumer<String>> callbackMap;
public static void put(String key, String value, Long timeout, Consumer<String> consumer) {
TIMED_CACHE.put(key, value, timeout);
addListen(key, consumer);
}
public static String get(String key) {
return TIMED_CACHE.get(key);
}
public static void remove(String key) {
callbackMap.remove(key);
TIMED_CACHE.remove(key);
}
public static void addListen(String key, Consumer<String> consumer) {
ListenableFuture<String> listenableFuture =
listeningExecutorService.submit(
() -> {
while (TIMED_CACHE.containsKey(key)) {
ThreadUtil.sleep(500);
}
return key;
});
Futures.addCallback(
listenableFuture,
new FutureCallback<String>() {
@Override
public void onSuccess(@Nullable String s) {
consumer.accept(s);
}
@Override
public void onFailure(Throwable throwable) {
throwable.printStackTrace();
}
},
listeningExecutorService);
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
put("haha", "1", 3000L, x -> System.out.println(MessageFormat.format("[{0}] - 缓存消逝", x)));
ThreadUtil.sleep(2000);
System.out.println(get("haha"));
ThreadUtil.sleep(2000);
System.out.println(get("haha"));
ThreadUtil.sleep(5000);
System.out.println(get("haha"));
// 关闭监听线程池
listeningExecutorService.shutdown();
}
}执行结果:
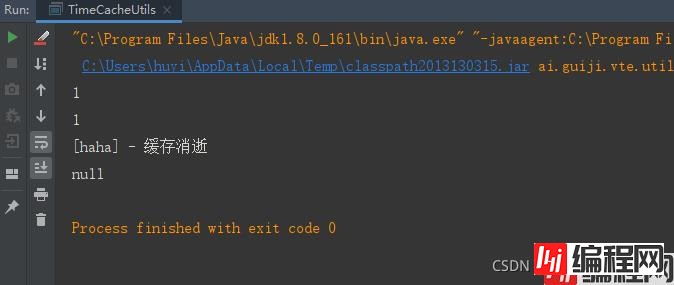
说明:
1、可以看到监听到缓存过期,并进行了回调。
具体的工具类使用场景,因项目而异,大家看着来。
如果本文对你有帮助,请点个赞支持一下吧。

到此这篇关于Java TimedCache 带时间缓存工具类详解使用的文章就介绍到这了,更多相关Java TimedCache内容请搜索编程网以前的文章或继续浏览下面的相关文章希望大家以后多多支持编程网!
--结束END--
本文标题: Java TimedCache 带时间缓存工具类详解使用
本文链接: https://www.lsjlt.com/news/155681.html(转载时请注明来源链接)
有问题或投稿请发送至: 邮箱/279061341@qq.com QQ/279061341
下载Word文档到电脑,方便收藏和打印~
2024-03-01
2024-03-01
2024-03-01
2024-02-29
2024-02-29
2024-02-29
2024-02-29
2024-02-29
2024-02-29
2024-02-29
回答
回答
回答
回答
回答
回答
回答
回答
回答
回答
0