Python 官方文档:入门教程 => 点击学习
目录一、对象单字段排序二、多字段排序三、数组排序以及List<Integer>排序一、对象单字段排序 List<People> peopleL
List<People> peopleList = Lists.newArrayList();
peopleList.add(new People(1, "小王", 5));
peopleList.add(new People(1, "小李", 4));
peopleList.add(new People(2, "小张", 3));
peopleList.add(new People(2, "小皇", 2));
peopleList.add(new People(2, "小刘", 1));
//单字段排序
peopleList = peopleList.stream().sorted(Comparator.comparing(People::getJgId)).collect(Collectors.toList());
log.info(peopleList.toString());
//这里是根据userId 进行排序——降序排序 reversed()
peopleList = peopleList.stream().sorted(Comparator.comparing(People::getJgId).reversed()).collect(Collectors.toList());
log.info(peopleList.toString());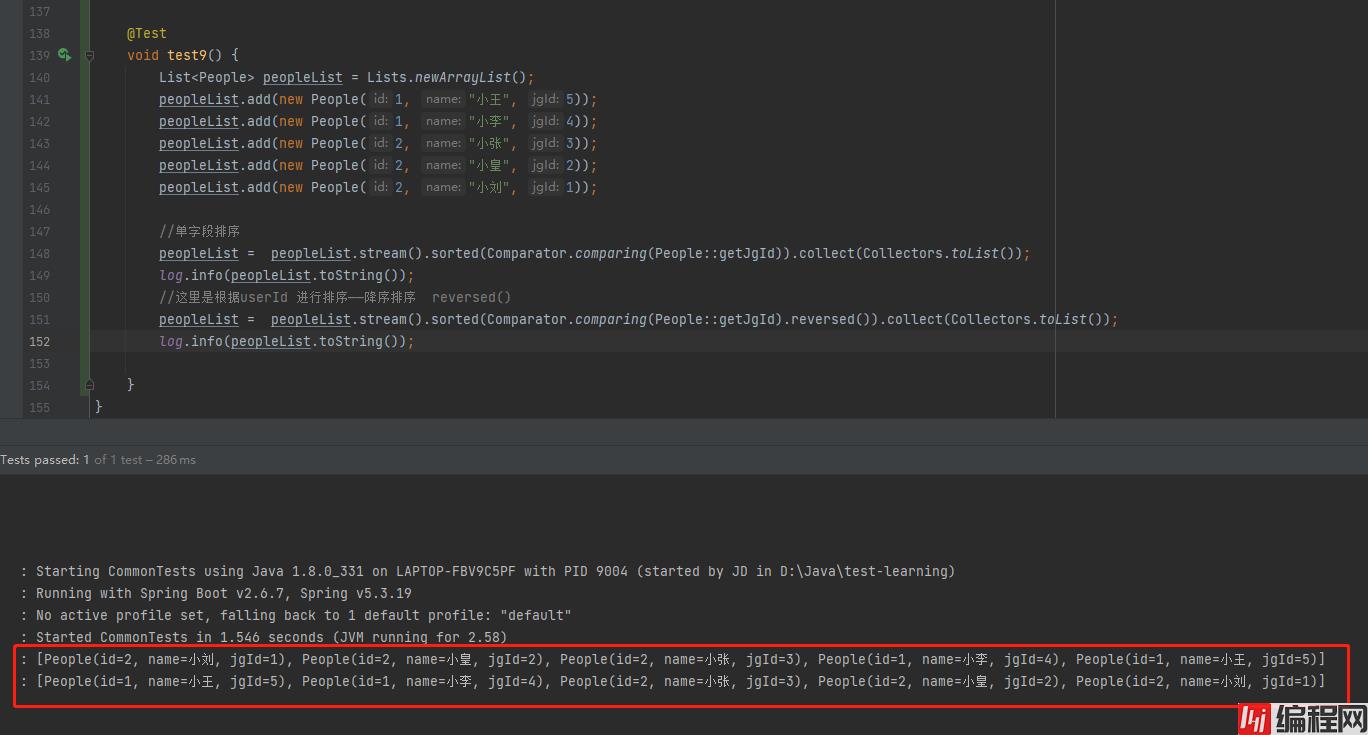
List<People> peopleList = Lists.newArrayList();
peopleList.add(new People(1, "小王", 5));
peopleList.add(new People(1, "小李", 4));
peopleList.add(new People(2, "小张", 3));
peopleList.add(new People(2, "小皇", 2));
peopleList.add(new People(2, "小刘", 1));
//这里是根据Id及jgId进行联合升序排序
peopleList = peopleList.stream().sorted(Comparator.comparing(People::getId).thenComparing(People::getJgId)).collect(Collectors.toList());
log.info(peopleList.toString());
//下面两个结果都是以Id降序jgId升序排序的结果,但是查询方式不同
//先以id升序,升序结果进行id降序,再进行jgId升序
peopleList = peopleList.stream().sorted(Comparator.comparing(People::getId).reversed().thenComparing(People::getJgId)).collect(Collectors.toList());
log.info(peopleList.toString());
//先以id降序,再进行jgId升序 **推荐使用该种方式**
peopleList = peopleList.stream().sorted(Comparator.comparing(People::getId,Comparator.reverseOrder()).thenComparing(People::getJgId)).collect(Collectors.toList());
log.info(peopleList.toString());
//先以id升序,再进行jgId降序
peopleList = peopleList.stream().sorted(Comparator.comparing(People::getId).thenComparing(People::getJgId,Comparator.reverseOrder())).collect(Collectors.toList());
log.info(peopleList.toString());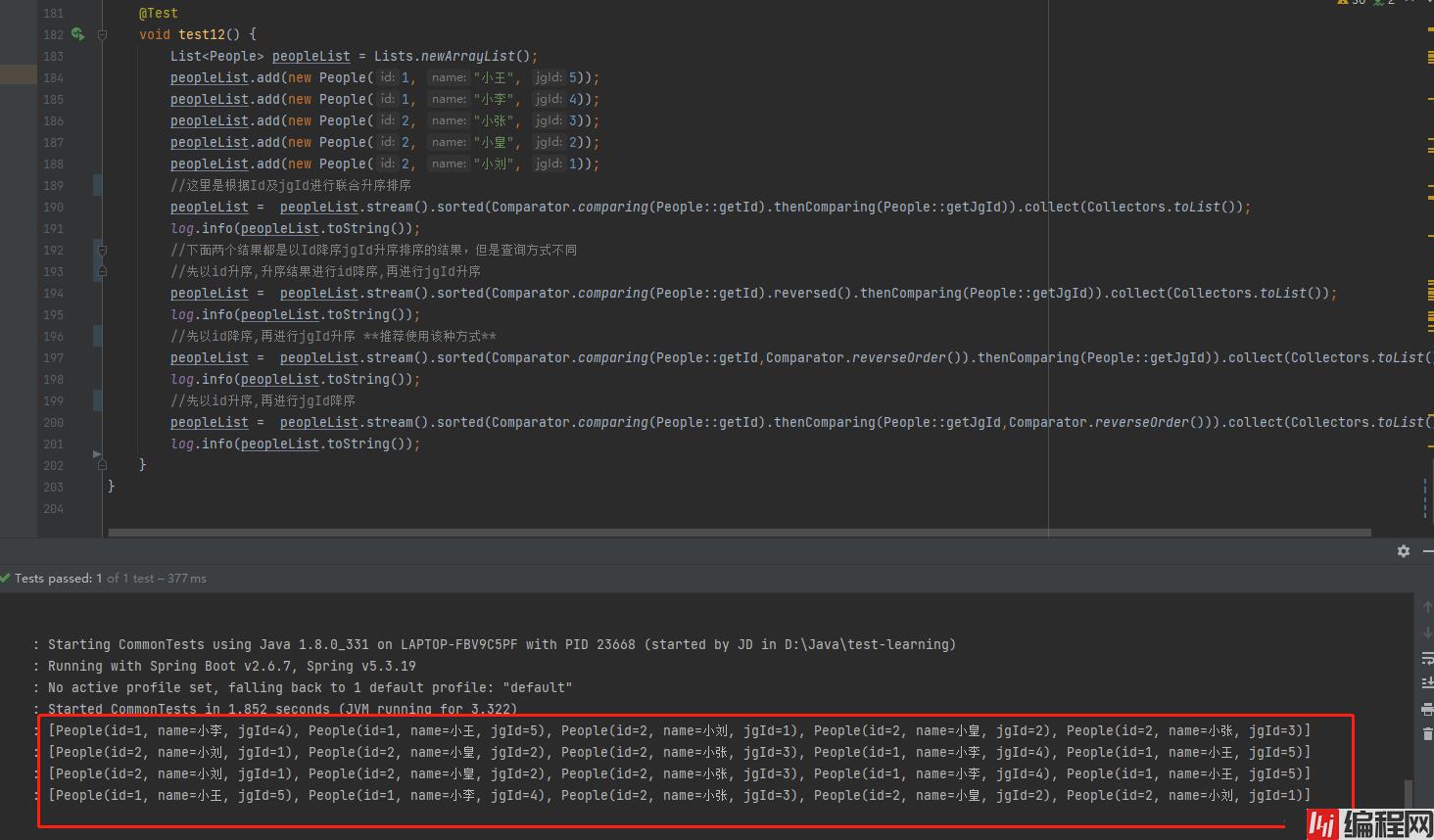
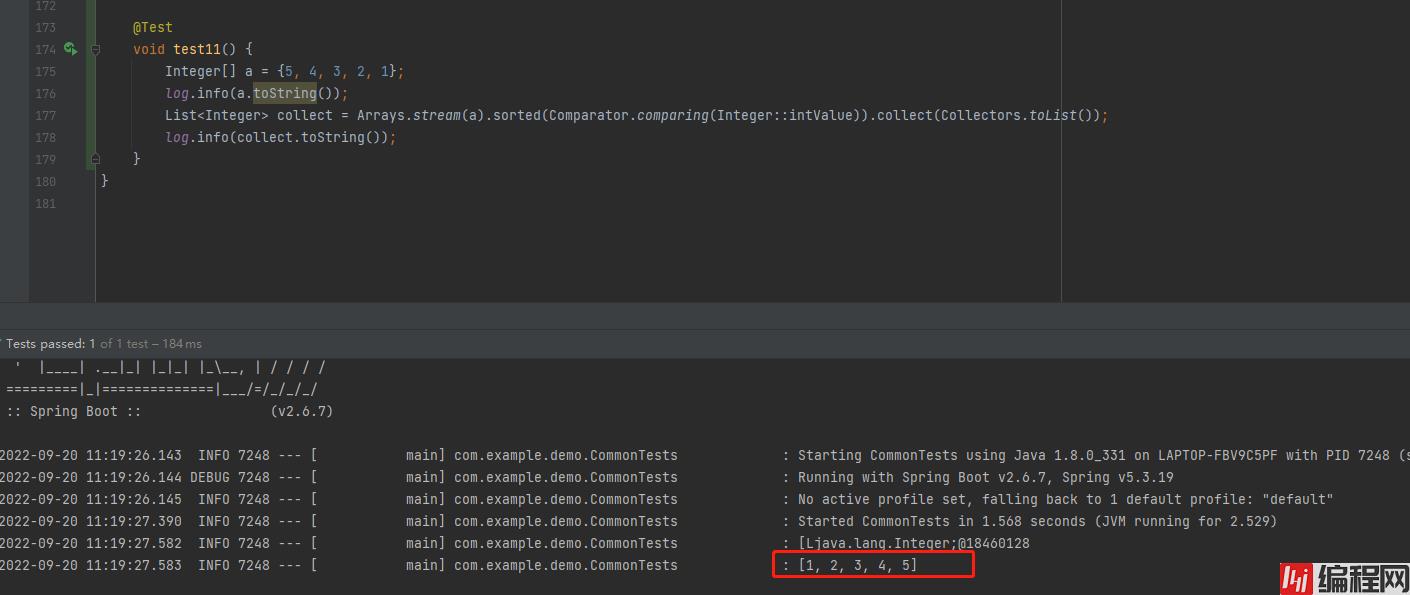
先把数组转换成List对象再进行排序
到此这篇关于Stream流排序数组和List 详解的文章就介绍到这了,更多相关Stream List 内容请搜索编程网以前的文章或继续浏览下面的相关文章希望大家以后多多支持编程网!
--结束END--
本文标题: Stream流排序数组和List 详解
本文链接: https://www.lsjlt.com/news/168059.html(转载时请注明来源链接)
有问题或投稿请发送至: 邮箱/279061341@qq.com QQ/279061341
下载Word文档到电脑,方便收藏和打印~
2024-03-01
2024-03-01
2024-03-01
2024-02-29
2024-02-29
2024-02-29
2024-02-29
2024-02-29
2024-02-29
2024-02-29
回答
回答
回答
回答
回答
回答
回答
回答
回答
回答
0