目录使用AxiOS发起POST请求提交文件React中fetch和axios的简单使用fetch的使用Axios的使用总结使用Axios发起POST请求提交文件 通过Axios发起P
通过Axios发起POST请求向后端提交文件
FORMData——传入文件类型参数
const formData = new FormData()
formData.append('key', value)下面是Axios的post操作
Axios({
headers: {
'Content-Type':'application/JSON'
},
method: 'post',
url:`后端url`,
data: formData,
onUploadProgress: ({total, loaded}) => {
files.onProgress({percent: Math.round((loaded/total)*100).toFixed(2)}, files)
}
}).then(res => {
if(res && res.status === 200){
// 响应成功的回调
message.success(fileName + '上传成功')
}else{
// 响应失败
}
})或者直接简单点,只需要URL与参数即可
Axios.post(`URL`, formData).then(res => {
if(res && res.status === 200){
// 成功时的回调
}else{
// 失败时的回调
}
})延伸:以下是axios的所有配置参数
axios({
// `url` 是用于请求的服务器 URL
url: '/user',
// `method` 是创建请求时使用的方法
method: 'get', // 默认是 get
// `baseURL` 将自动加在 `url` 前面,除非 `url` 是一个绝对 URL。
// 它可以通过设置一个 `baseURL` 便于为 axios 实例的方法传递相对 URL
baseURL: 'https://some-domain.com/api/',
// `transformRequest` 允许在向服务器发送前,修改请求数据
// 只能用在 'PUT', 'POST' 和 'PATCH' 这几个请求方法
// 后面数组中的函数必须返回一个字符串,或 ArrayBuffer,或 Stream
transformRequest: [function (data) {
// 对 data 进行任意转换处理
return data;
}],
// `transformResponse` 在传递给 then/catch 前,允许修改响应数据
transformResponse: [function (data) {
// 对 data 进行任意转换处理
return data;
}],
// `headers` 是即将被发送的自定义请求头
headers: { 'X-Requested-With': 'XMLHttpRequest' },
// `params` 是即将与请求一起发送的 URL 参数
// 必须是一个无格式对象(plain object)或 URLSearchParams 对象
params: {
ID: 12345
},
// `paramsSerializer` 是一个负责 `params` 序列化的函数
// (e.g. https://www.npmjs.com/package/qs, http://api.Jquery.com/jquery.param/)
paramsSerializer: function (params) {
return Qs.stringify(params, { arrayFormat: 'brackets' })
},
// `data` 是作为请求主体被发送的数据
// 只适用于这些请求方法 'PUT', 'POST', 和 'PATCH'
// 在没有设置 `transformRequest` 时,必须是以下类型之一:
// - string, plain object, ArrayBuffer, ArrayBufferView, URLSearchParams
// - 浏览器专属:FormData, File, Blob
// - node 专属: Stream
data: {
firstName: 'Fred'
},
// `timeout` 指定请求超时的毫秒数(0 表示无超时时间)
// 如果请求话费了超过 `timeout` 的时间,请求将被中断
timeout: 1000,
// `withCredentials` 表示跨域请求时是否需要使用凭证
withCredentials: false, // 默认的
// `adapter` 允许自定义处理请求,以使测试更轻松
// 返回一个 promise 并应用一个有效的响应 (查阅 [response docs](#response-api)).
adapter: function (config) {
},
// `auth` 表示应该使用 HTTP 基础验证,并提供凭据
// 这将设置一个 `Authorization` 头,覆写掉现有的任意使用 `headers` 设置的自
定义 `Authorization`头
auth: {
username: 'janedoe',
passWord: 's00pers3cret'
},
// `responseType` 表示服务器响应的数据类型,
可以是 'arraybuffer', 'blob', 'document', 'json', 'text', 'stream'
responseType: 'json', // 默认的
// `xsrfCookieName` 是用作 xsrf token 的值的cookie的名称
xsrfCookieName: 'XSRF-TOKEN', // default
// `xsrfHeaderName` 是承载 xsrf token 的值的 HTTP 头的名称
xsrfHeaderName: 'X-XSRF-TOKEN', // 默认的
// `onUploadProgress` 允许为上传处理进度事件
onUploadProgress: function (progressEvent) {
// 对原生进度事件的处理
},
// `onDownloadProgress` 允许为下载处理进度事件
onDownloadProgress: function (progressEvent) {
// 对原生进度事件的处理
},
// `maxContentLength` 定义允许的响应内容的最大尺寸
maxContentLength: 2000,
// `validateStatus` 定义对于给定的HTTP 响应状态码是 resolve 或
reject promise 。如果 `validateStatus` 返回 `true`
(或者设置为 `null` 或 `undefined`),promise 将被 resolve; 否则,promise 将被 rejecte
validateStatus: function (status) {
return status >= 200 && status < 300; // 默认的
},
// `maxRedirects` 定义在 node.js 中 follow 的最大重定向数目
// 如果设置为0,将不会 follow 任何重定向
maxRedirects: 5, // 默认的
// `httpAgent` 和 `httpsAgent` 分别在 node.js 中用于定义在执行 http 和
https 时使用的自定义代理。允许像这样配置选项:
// `keepAlive` 默认没有启用
httpAgent: new http.Agent({ keepAlive: true }),
httpsAgent: new https.Agent({ keepAlive: true }),
// 'proxy' 定义代理服务器的主机名称和端口
// `auth` 表示 HTTP 基础验证应当用于连接代理,并提供凭据
// 这将会设置一个 `Proxy-Authorization` 头,覆写掉已有的通过使用 `header`
设置的自定义 `Proxy-Authorization` 头。
proxy: {
host: '127.0.0.1',
port: 9000,
auth: : {
username: 'mikeymike',
password: 'rapunz3l'
}
},
// `cancelToken` 指定用于取消请求的 cancel token
// (查看后面的 Cancellation 这节了解更多)
cancelToken: new CancelToken(function (cancel) {
})
})废话不多说,我们先看看文档(看不懂也无所谓的OAO!!)
文档:whatwg-fetch - npm
1.安装 cd到你创建react项目的目录,在终端输入:
npm install whatwg-fetch --save2. npm start
3.在public下面创建一个叫做 user.json 的文件,代码如下:
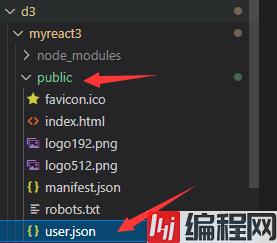
[
{
"stuNo":"007",
"stuName":"double",
"stuSex":0,
"salary":100000
},
{
"stuNo":"008",
"stuName":"liu",
"stuSex":0,
"salary":200000
},
{
"stuNo":"009",
"stuName":"li",
"stuSex":1,
"salary":100000
}
]4.创建一个名为 UserManage.js 的组件,代码如下:
因为咱们src里面的App.js最终编译到 public 里面的 index.html,所以路径才这样写!
import React, { Component } from 'react';
import "whatwg-fetch"
class UserManage extends Component {
componentDidMount(){
fetch("/user.json").then((response)=>{
return response.json()
}).then((res)=>{
console.log(res)
}).catch((err)=>{
console.log(err)
})
}
render() {
return (
<div>
<h2>用户管理</h2>
</div>
);
}
}
export default UserManage;第一个 then 是把response返回来的数据转换为json格式,第二个 then 里面的数据才是我们需要的内容。
4.查看控制台
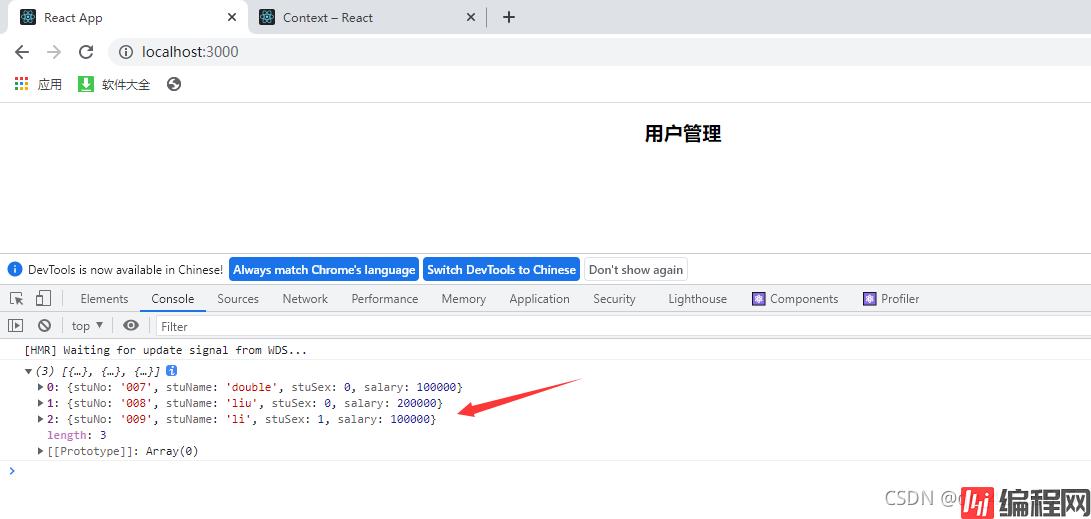
这就是咱们得到的res。
那么,我们怎么在react中发起一个简单的axios请求呢?
1.先搭建一个node。不会搭建?没关系,手把手教学。先创建一个叫 nodeproject的文件夹。
再创建一个叫 package.json的文件,再创建一个叫 app.js的文件。
以下是package.json的代码:
{
"name": "nodejsproject",
"version": "1.0.0",
"description": "",
"main": "app.js",
"scripts": {
"test": "echo \"Error: no test specified\" && exit 1"
},
"author": "",
"license": "ISC",
"dependencies": {
"body-parser": "^1.19.0",
"express": "^4.17.1",
"morgan": "^1.10.0",
"Mysql": "^2.18.1"
},
"devDependencies": {
"serve-favicon": "^2.5.0"
}
}以下是app.js的代码:
const myexpress = require('express');
const path = require("path");
const logger = require('morgan');
const favicon = require('serve-favicon');
const bodyParser = require('body-parser');
const app = myexpress();
// 跨域
app.all("*",function(req,res,next){
res.header("Access-Control-Allow-Origin","*");
res.header("Access-Control-Allow-Headers", "X-Requested-With,X_Requested_With,Content-Type");
next();
})
// 定义日志和输出级别
app.use(logger('dev'));
// 必须设置在静态资源文件目录的前面,否则看不到日志的输出
app.use(myexpress.static(path.join(__dirname,"public"),{index:"login.html"}));
// 定义icon图标
// app.use(favicon(__dirname + '/public/favicon.ico'));
// 定义数据解析器 这个要放在post的前面
app.use(bodyParser.json());
app.use(bodyParser.urlencoded({ extended: false }));
app.post("/studentDetail",function(req,res){
res.send(
{student:
[
{
"stuNo":"007",
"stuName":"double",
"stuSex":0,
"salary":100000
},
{
"stuNo":"008",
"stuName":"liu",
"stuSex":0,
"salary":200000
},
{
"stuNo":"009",
"stuName":"li",
"stuSex":1,
"salary":100000
}
]
}
)
})
app.listen(7777,function(){
console.log("服务已启动");
})
(笔者已经把post请求写好了)
然后在控制台运行命令:
npm i
就可以把package.json里的工具下载下来。再启动node,搞定~

3.在发送axios请求前,我们再试试用fetch发送请求。
看文档找到了写法~
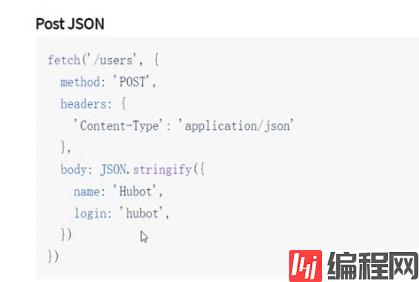
咱们也照葫芦画瓢,UserManage.js的代码为:
import React, { Component } from 'react';
import "whatwg-fetch"
class UserManage extends Component {
componentDidMount(){
fetch("http://localhost:7777/studentDetail",
{
method:'POST',
headers:{
'Content-Type':'application/json'
},
body:JSON.stringify({
name:'Hubot',
login:'hubot',
})
}).then((response)=>{
return response.json()
}).then((res)=>{
console.log(res)
}).catch((err)=>{
console.log(err)
})
}
render() {
return (
<div>
<h2>用户管理</h2>
</div>
);
}
}
export default UserManage;4.运行就看到效果啦~成功~
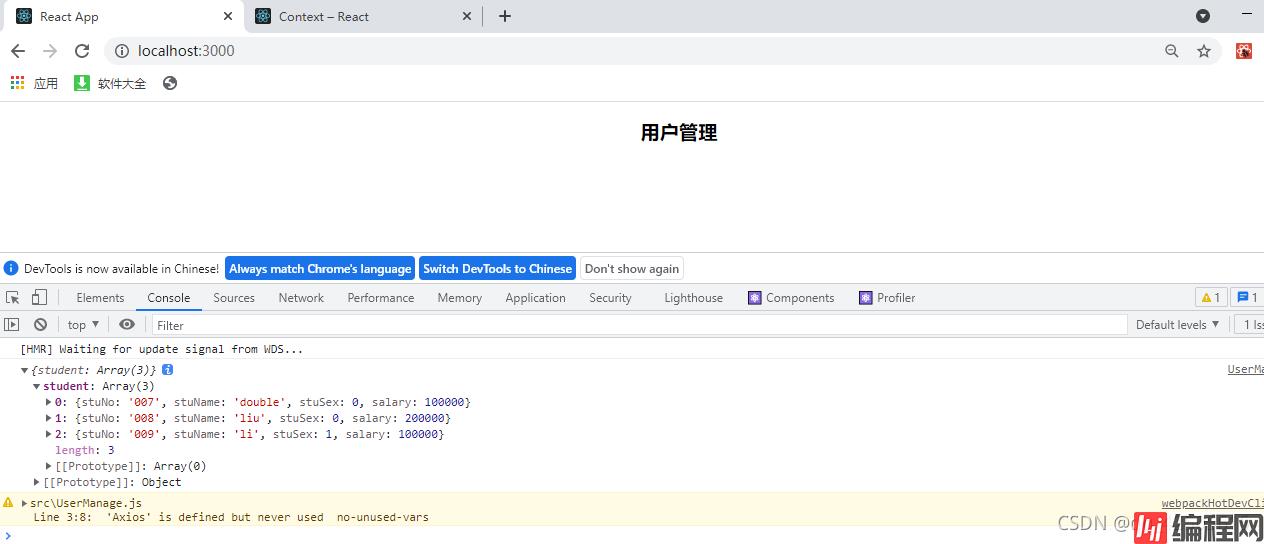
可能有朋友觉得每次写域名都写一大串,太麻烦,干脆我们把它提取出来。
在src目录下我们创建一个叫 config.js 的文件。
代码如下:
export const host_url = "http://localhost:7777"然后回到 UserManage.js文件中,我们引入它:
import {host_url} from './config'就只需要改一下下面的内容,效果是一样的~
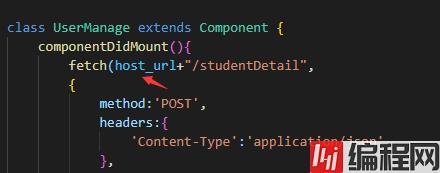
5.好了~正式进入到axios的学习,有了前面的铺垫,现在特别简单。我们先下载axios。
npm i axios
下好后引入:
import Axios from 'axios'UserManage.js的代码如下:
import React, { Component } from 'react';
import {host_url} from './config'
import "whatwg-fetch"
import Axios from 'axios'
class UserManage extends Component {
componentDidMount(){
Axios.post(host_url+"/studentDetail").then((res)=>{
console.log(res.data.student)
}).catch((err)=>{
console.log(err)
})
}
render() {
return (
<div>
<h2>用户管理</h2>
</div>
);
}
}
export default UserManage;也是一样的能访问到数据,好了,写完了,撒花~
以上为个人经验,希望能给大家一个参考,也希望大家多多支持编程网。
--结束END--
本文标题: React中使用Axios发起POST请求提交文件方式
本文链接: https://www.lsjlt.com/news/195777.html(转载时请注明来源链接)
有问题或投稿请发送至: 邮箱/279061341@qq.com QQ/279061341
下载Word文档到电脑,方便收藏和打印~
2024-01-12
2023-05-20
2023-05-20
2023-05-20
2023-05-20
2023-05-20
2023-05-20
2023-05-20
2023-05-20
2023-05-20
回答
回答
回答
回答
回答
回答
回答
回答
回答
回答
0