这篇文章主要讲解了“Kotlin协程切换为线程的方法”,文中的讲解内容简单清晰,易于学习与理解,下面请大家跟着小编的思路慢慢深入,一起来研究和学习“Kotlin协程切换为线程的方法”吧!随着kotlin在Android开发领域越来越火,协程
这篇文章主要讲解了“Kotlin协程切换为线程的方法”,文中的讲解内容简单清晰,易于学习与理解,下面请大家跟着小编的思路慢慢深入,一起来研究和学习“Kotlin协程切换为线程的方法”吧!
随着kotlin在Android开发领域越来越火,协程在各个项目中的应用也逐渐变得广泛
但是协程到底是什么呢?
协程其实是个古老的概念,已经非常成熟了,但大家对它的概念一直存在各种疑问,众说纷纷
有人说协程是轻量级的线程,也有人说kotlin协程其实本质是一套线程切换方案
显然这对初学者不太友好,当不清楚一个东西是什么的时候,就很难进入为什么和怎么办的阶段了
本文主要就是回答这个问题,主要包括以下内容
关于协程的一些前置知识
2.协程到底是什么?
3.kotlin协程的一些基本概念,挂起函数,CPS转换,状态机等
以上问题总结为思维导图如下:
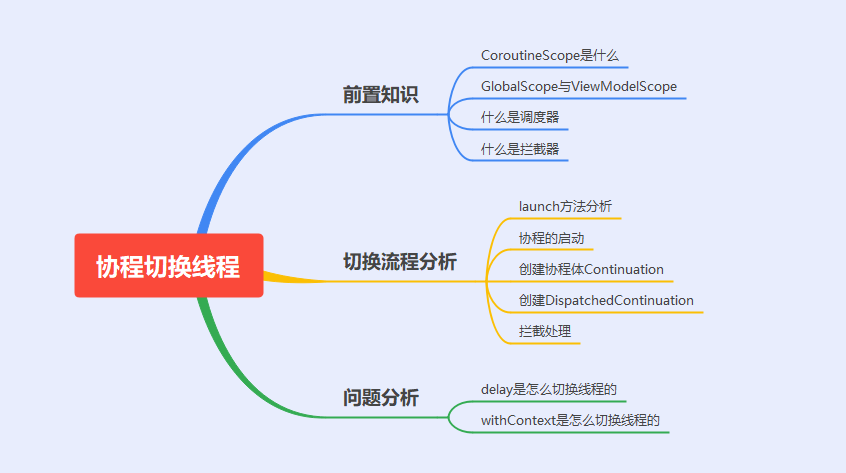
1 CoroutineScope到底是什么?
CoroutineScope即协程运行的作用域,它的源码很简单
public interface CoroutineScope { public val coroutineContext: CoroutineContext}可以看出CoroutineScope的代码很简单,主要作用是提供CoroutineContext,协程运行的上下文
我们常见的实现有GlobalScope,LifecycleScope,ViewModelScope等
2 GlobalScope与ViewModelScope有什么区别?
public object GlobalScope : CoroutineScope { override val coroutineContext: CoroutineContext get() = EmptyCoroutineContext}public val ViewModel.viewModelScope: CoroutineScope get() { val scope: CoroutineScope? = this.getTag(JOB_KEY) if (scope != null) { return scope } return setTagIfAbsent( JOB_KEY, CloseableCoroutineScope(SupervisorJob() + Dispatchers.Main.immediate) ) }两者的代码都挺简单,从上面可以看出
1.GlobalScope返回的为CoroutineContext的空实现
2.ViewModelScope则往CoroutineContext中添加了Job与Dispatcher
我们先来看一段简单的代码
fun testOne(){GlobalScope.launch { print("1:" + Thread.currentThread().name) delay(1000) print("2:" + Thread.currentThread().name) }}//打印结果为:DefaultDispatcher-worker-1 fun testTwo(){ viewModelScope.launch { print("1:" + Thread.currentThread().name) delay(1000) print("2:" + Thread.currentThread().name) } } //打印结果为: main上面两种Scope启动协程后,打印当前线程名是不同的,一个是线程池中的一个线程,一个则是主线程
这是因为ViewModelScope在CoroutineContext中添加了Dispatchers.Main.immediate的原因
我们可以得出结论:协程就是通过Dispatchers调度器来控制线程切换的
3 什么是调度器?
从使用上来讲,调度器就是我们使用的Dispatchers.Main,Dispatchers.Default,Dispatcher.io等
从作用上来讲,调度器的作用是控制协程运行的线程
从结构上来讲,Dispatchers的父类是ContinuationInterceptor,然后再继承于CoroutineContext
它们的类结构关系如下:
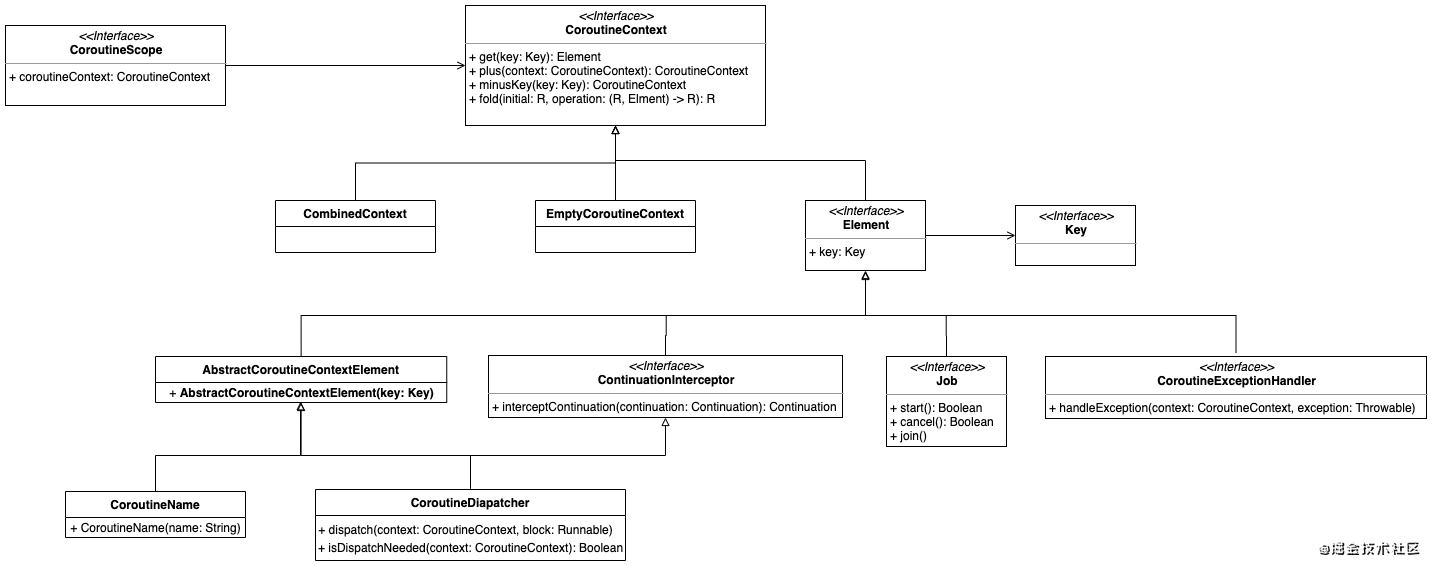
这也是为什么Dispatchers能加入到CoroutineContext中的原因,并且支持+操作符来完成增加
4 什么是拦截器
从命名上很容易看出,ContinuationInterceptor即协程拦截器,先看一下接口
interface ContinuationInterceptor : CoroutineContext.Element { // ContinuationInterceptor 在 CoroutineContext 中的 Key compaNIOn object Key : CoroutineContext.Key<ContinuationInterceptor> fun <T> interceptContinuation(continuation: Continuation<T>): Continuation<T> //...}从上面可以提炼出两个信息
1.拦截器的Key是单例的,因此当你添加多个拦截器时,生效的只会有一个
2.我们都知道,Continuation在调用其Continuation#resumeWith()方法,会执行其suspend修饰的函数的代码块,如果我们提前拦截到,是不是可以做点其他事情?这就是调度器切换线程的原理
上面我们已经介绍了是通过Dispatchers指定协程运行的线程,通过interceptContinuation在协程恢复前进行拦截,从而切换线程
带着这些前置知识,我们一起来看下协程启动的具体流程,明确下协程切换线程源码具体实现
1 launch方法解析
我们首先看一下协程是怎样启动的,传入了什么参数
public fun CoroutineScope.launch( context: CoroutineContext = EmptyCoroutineContext, start: CoroutineStart = CoroutineStart.DEFAULT, block: suspend CoroutineScope.() -> Unit): Job { val newContext = newCoroutineContext(context) val coroutine = if (start.isLazy) LazyStandaloneCoroutine(newContext, block) else StandaloneCoroutine(newContext, active = true) coroutine.start(start, coroutine, block) return coroutine}总共有3个参数:
1.传入的协程上下文
2.CoroutinStart启动器,是个枚举类,定义了不同的启动方法,默认是CoroutineStart.DEFAULT
3.block就是我们传入的协程体,真正要执行的代码
这段代码主要做了两件事:
1.组合新的CoroutineContext
2.再创建一个 Continuation
1.1 组合新的CoroutineContext
public actual fun CoroutineScope.newCoroutineContext(context: CoroutineContext): CoroutineContext { val combined = coroutineContext + context val debug = if (DEBUG) combined + CoroutineId(COROUTINE_ID.incrementAndGet()) else combined return if (combined !== Dispatchers.Default && combined[ContinuationInterceptor] == null) debug + Dispatchers.Default else debug}从上面可以提炼出以下信息:
1.会将launch方法传入的context与CoroutineScope中的context组合起来
2.如果combined中没有拦截器,会传入一个默认的拦截器,即Dispatchers.Default,这也解释了为什么我们没有传入拦截器时会有一个默认切换线程的效果
1.2 创建一个Continuation
val coroutine = if (start.isLazy) LazyStandaloneCoroutine(newContext, block) else StandaloneCoroutine(newContext, active = true) coroutine.start(start, coroutine, block)默认情况下,我们会创建一个StandloneCoroutine
值得注意的是,这个coroutine其实是我们协程体的complete,即成功后的回调,而不是协程体本身
然后调用coroutine.start,这表明协程开始启动了
2 协程的启动
public fun <R> start(start: CoroutineStart, receiver: R, block: suspend R.() -> T) { initParentJob() start(block, receiver, this)}接着调用CoroutineStart的start来启动协程,默认情况下调用的是CoroutineStart.Default
经过层层调用,最后到达了:
internal fun <R, T> (suspend (R) -> T).startCoroutineCancellable(receiver: R, completion: Continuation<T>) = runSafely(completion) { // 外面再包一层 Coroutine createCoroutineUnintercepted(receiver, completion) // 如果需要,做拦截处理 .intercepted() // 调用 resumeWith 方法 .resumeCancellableWith(Result.success(Unit)) }这里就是协程启动的核心代码,虽然比较短,却包括3个步骤:
1.创建协程体Continuation
2.创建拦截 Continuation,即DispatchedContinuation
3.执行DispatchedContinuation.resumeWith方法
3 创建协程体Continuation
调用createCoroutineUnintercepted,会把我们的协程体即suspend block转换成Continuation,它是SuspendLambda,继承自ContinuationImplcreateCoroutineUnintercepted方法在源码中找不到具体实现,不过如果你把协程体代码反编译后就可以看到真正的实现
详情可见:字节码反编译
4 创建DispatchedContinuation
public actual fun <T> Continuation<T>.intercepted(): Continuation<T> = (this as? ContinuationImpl)?.intercepted() ?: this//ContinuationImplpublic fun intercepted(): Continuation<Any?> = intercepted ?: (context[ContinuationInterceptor]?.interceptContinuation(this) ?: this) .also { intercepted = it } //CoroutineDispatcherpublic final override fun <T> interceptContinuation(continuation: Continuation<T>): Continuation<T> = DispatchedContinuation(this, continuation)从上可以提炼出以下信息
1.interepted是个扩展方法,最后会调用到ContinuationImpl.intercepted方法
2.在intercepted会利用CoroutineContext,获取当前的拦截器
3.因为当前的拦截器是CoroutineDispatcher,因此最终会返回一个DispatchedContinuation,我们其实也是利用它实现线程切换的
4.我们将协程体的Continuation传入DispatchedContinuation,这里其实用到了装饰器模式,实现功能的增强
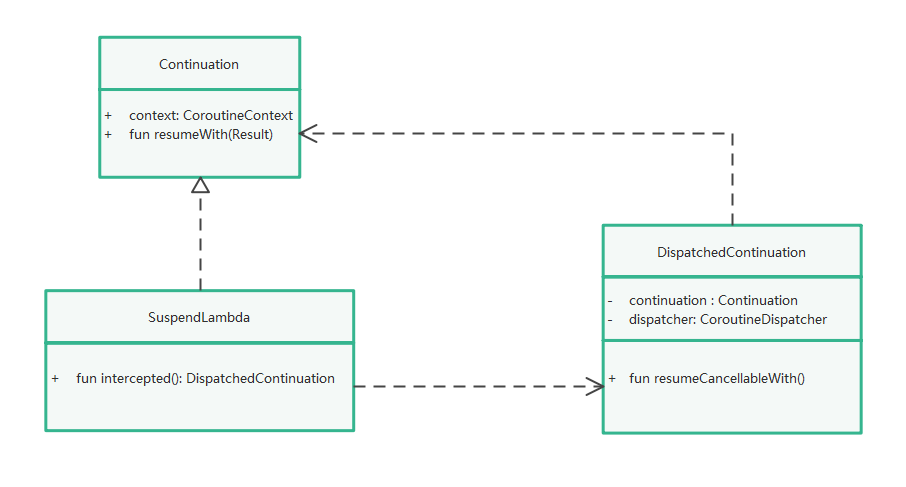
这里其实很明显了,通过DispatchedContinuation装饰原有协程,在DispatchedContinuation里通过调度器处理线程切换,不影响原有逻辑,实现功能的增强
5 拦截处理
//DispatchedContinuation inline fun resumeCancellableWith( result: Result<T>, noinline onCancellation: ((cause: Throwable) -> Unit)? ) { val state = result.toState(onCancellation) if (dispatcher.isDispatchNeeded(context)) { _state = state resumeMode = MODE_CANCELLABLE dispatcher.dispatch(context, this) } else { executeUnconfined(state, MODE_CANCELLABLE) { if (!resumeCancelled(state)) { resumeUndispatchedWith(result) } } } }上面说到了启动时会调用DispatchedContinuation的resumeCancellableWith方法
这里面做的事也很简单:
1.如果需要切换线程,调用dispatcher.dispatcher方法,这里的dispatcher是通过CoroutineConext取出来的
2.如果不需要切换线程,直接运行原有线程即可
2 调度器的具体实现
我们首先明确下,CoroutineDispatcher是通过CoroutineContext取出来的,这也是协程上下文作用的体现CoroutineDispater官方提供了四种实现:Dispatchers.Main,Dispatchers.IO,Dispatchers.Default,Dispatchers.Unconfined
我们一起简单看下Dispatchers.Main的实现
internal class HandlerContext private constructor( private val handler: Handler, private val name: String?, private val invokeImmediately: Boolean) : HandlerDispatcher(), Delay { public constructor( handler: Handler, name: String? = null ) : this(handler, name, false) //... override fun dispatch(context: CoroutineContext, block: Runnable) { // 利用主线程的 Handler 执行任务 handler.post(block) }}可以看到,其实就是用handler切换到了主线程
如果用Dispatcers.IO也是一样的,只不过换成线程池切换了
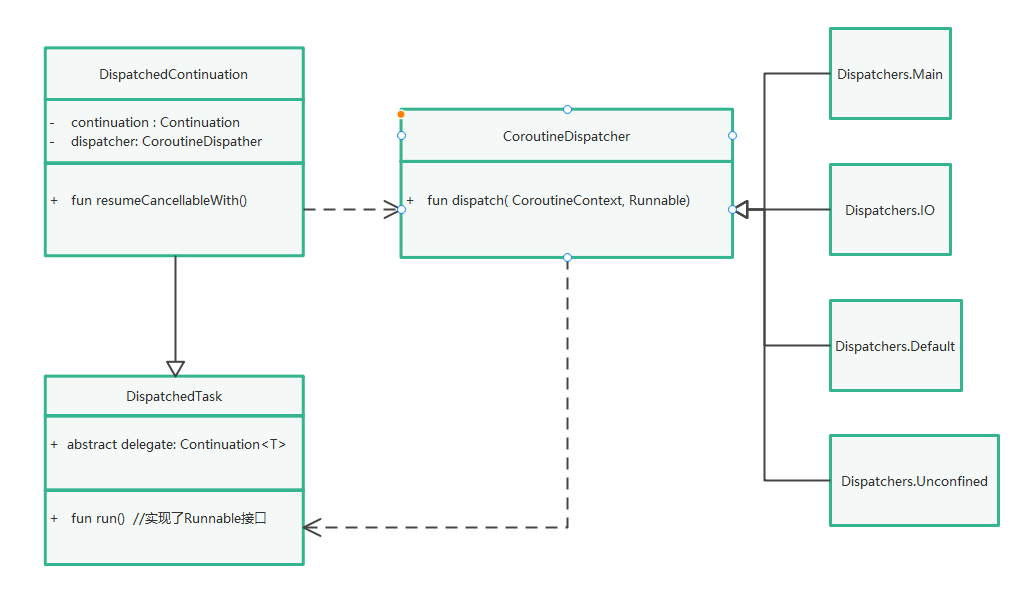
如上所示,其实就是一个装饰模式
1.调用CoroutinDispatcher.dispatch方法切换线程
2.切换完成后调用DispatchedTask.run方法,执行真正的协程体
3 delay是怎样切换线程的?
上面我们介绍了协程线程调度的基本原理与实现,下面我们来回答几个小问题
我们知道delay函数会挂起,然后等待一段时间再恢复。
可以想象,这里面应该也涉及到线程的切换,具体是怎么实现的呢?
public suspend fun delay(timeMillis: Long) { if (timeMillis <= 0) return // don't delay return suspendCancellableCoroutine sc@ { cont: CancellableContinuation<Unit> -> // if timeMillis == Long.MAX_VALUE then just wait forever like awaitCancellation, don't schedule. if (timeMillis < Long.MAX_VALUE) { cont.context.delay.scheduleResumeAfterDelay(timeMillis, cont) } }}internal val CoroutineContext.delay: Delay get() = get(ContinuationInterceptor) as? Delay ?: DefaultDelayDealy的代码也很简单,从上面可以提炼出以下信息delay的切换也是通过拦截器来实现的,内置的拦截器同时也实现了Delay接口
我们来看一个具体实现
internal class HandlerContext private constructor( private val handler: Handler, private val name: String?, private val invokeImmediately: Boolean) : HandlerDispatcher(), Delay { override fun scheduleResumeAfterDelay(timeMillis: Long, continuation: CancellableContinuation<Unit>) { // 利用主线程的 Handler 延迟执行任务,将完成的 continuation 放在任务中执行 val block = Runnable { with(continuation) { resumeUndispatched(Unit) } } handler.postDelayed(block, timeMillis.coerceAtMost(MAX_DELAY)) continuation.invokeOnCancellation { handler.removeCallbacks(block) } } //..}可以看出,其实也是通过handler.postDelayed实现延时效果的
2.时间到了之后,再通过resumeUndispatched方法恢复协程
3.如果我们用的是Dispatcher.IO,效果也是一样的,不同的就是延时效果是通过切换线程实现的
withContext是怎样切换线程的?
我们在协程体内,可能通过withContext方法简单便捷的切换线程,用同步的方式写异步代码,这也是kotin协程的主要优势之一
fun test(){ viewModelScope.launch(Dispatchers.Main) { print("1:" + Thread.currentThread().name) withContext(Dispatchers.IO){ delay(1000) print("2:" + Thread.currentThread().name) } print("3:" + Thread.currentThread().name) } } //1,2,3处分别输出main,DefaultDispatcher-worker-1,main可以看出这段代码做了一个切换线程然后再切换回来的操作,我们可以提出两个问题
1.withContext是怎样切换线程的?
2.withContext内的协程体结束后,线程怎样切换回到Dispatchers.Main?
public suspend fun <T> withContext( context: CoroutineContext, block: suspend CoroutineScope.() -> T): T { return suspendCoroutineUninterceptedOrReturn sc@ { uCont -> // 创建新的context val oldContext = uCont.context val newContext = oldContext + context .... //使用新的Dispatcher,覆盖外层 val coroutine = DispatchedCoroutine(newContext, uCont) coroutine.initParentJob() //DispatchedCoroutine作为了complete传入 block.startCoroutineCancellable(coroutine, coroutine) coroutine.getResult() }}private class DispatchedCoroutine<in T>( context: CoroutineContext, uCont: Continuation<T>) : ScopeCoroutine<T>(context, uCont) {//在complete时会会回调 override fun afterCompletion(state: Any?) { afterResume(state) } override fun afterResume(state: Any?) { //uCont就是父协程,context仍是老版context,因此可以切换回原来的线程上 uCont.intercepted().resumeCancellableWith(recoverResult(state, uCont)) }}这段代码其实也很简单,可以提炼出以下信息
1.withContext其实就是一层api封装,最后调用到了startCoroutineCancellable,这就跟launch后面的流程一样了,我们就不继续跟了
2.传入的context会覆盖外层的拦截器并生成一个newContext,因此可以实现线程的切换
3.DispatchedCoroutine作为complete传入协程体的创建函数中,因此协程体执行完成后会回调到afterCompletion中
4.DispatchedCoroutine中传入的uCont是父协程,它的拦截器仍是外层的拦截器,因此会切换回原来的线程中
总结
本文主要回答了kotlin协程到底是怎么切换线程的这个问题,并对源码进行了分析
简单来讲主要包括以下步骤:
1.向CoroutineContext添加Dispatcher,指定运行的协程
2.在启动时将suspend block创建成Continuation,并调用intercepted生成DispatchedContinuation
3.DispatchedContinuation就是对原有协程的装饰,在这里调用Dispatcher完成线程切换任务后,resume被装饰的协程,就会执行协程体内的代码了
其实kotlin协程就是用装饰器模式实现线程切换的
看起来似乎有不少代码,但是真正的思路其实还是挺简单的,这大概就是设计模式的作用吧
感谢各位的阅读,以上就是“Kotlin协程切换为线程的方法”的内容了,经过本文的学习后,相信大家对Kotlin协程切换为线程的方法这一问题有了更深刻的体会,具体使用情况还需要大家实践验证。这里是编程网,小编将为大家推送更多相关知识点的文章,欢迎关注!
--结束END--
本文标题: Kotlin协程切换为线程的方法
本文链接: https://www.lsjlt.com/news/297757.html(转载时请注明来源链接)
有问题或投稿请发送至: 邮箱/279061341@qq.com QQ/279061341
下载Word文档到电脑,方便收藏和打印~
2024-05-24
2024-05-24
2024-05-24
2024-05-24
2024-05-24
2024-05-24
2024-05-24
2024-05-24
2024-05-24
2024-05-24
回答
回答
回答
回答
回答
回答
回答
回答
回答
回答
0