Python 官方文档:入门教程 => 点击学习
今天就跟大家聊聊有关python中怎么利用Dijkstra算法规划机器人路径,可能很多人都不太了解,为了让大家更加了解,小编给大家总结了以下内容,希望大家根据这篇文章可以有所收获。一、算法原理如图所示,Dijkstra算法要解决的是一个有向
今天就跟大家聊聊有关python中怎么利用Dijkstra算法规划机器人路径,可能很多人都不太了解,为了让大家更加了解,小编给大家总结了以下内容,希望大家根据这篇文章可以有所收获。
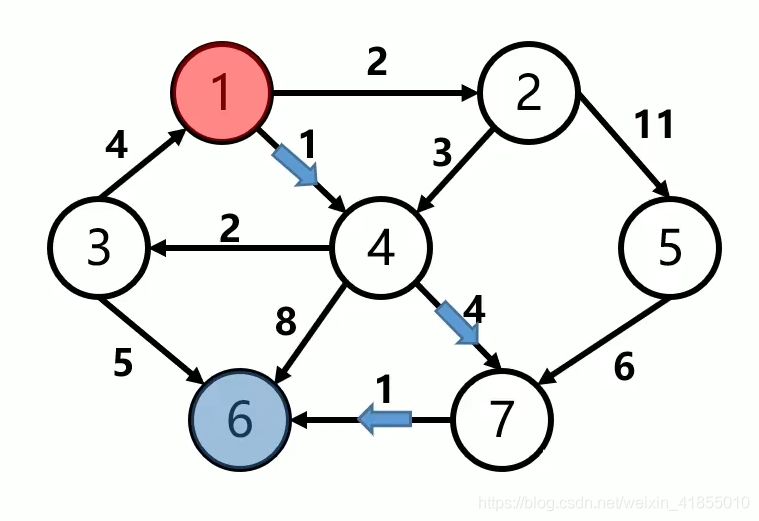
如图所示,Dijkstra算法要解决的是一个有向权重图中最短路径的寻找问题,图中红色节点1代表起始节点,蓝色节点6代表目标结点。箭头上的数字代表两个结点中的的距离,也就是模型中所谓的代价(cost)。
贪心算法需要设立两个集合,open_set(开集)和closed_set(闭集),然后根据以下程序进行操作:
把初始结点放入到open_set中;
把open_set中代价最小的节点取出来放入到closed_set中,并且作为当前节点;
把与当前节点相邻的节点放入到open_set中,如果代价更小更新代价
重复2-3过程,直到找到终点。
注意open_set中的代价是可变的,而closed_set中的代价已经是最小的代价了,这也是为什么叫做open和close的原因。
至于为什么closed_set中的代价是最小的,是因为我们使用了贪心算法,既然已经把节点加入到了close中,那么初始点到close节点中的距离就比到open中的距离小了,无论如何也不可能找到比它更小的了。
"""Grid based Dijkstra planningauthor: Atsushi Sakai(@Atsushi_twi)"""import matplotlib.pyplot as pltimport mathshow_animation = Trueclass Dijkstra: def __init__(self, ox, oy, resolution, robot_radius): """ Initialize map for a star planning ox: x position list of Obstacles [m] oy: y position list of Obstacles [m] resolution: grid resolution [m] rr: robot radius[m] """ self.min_x = None self.min_y = None self.max_x = None self.max_y = None self.x_width = None self.y_width = None self.obstacle_map = None self.resolution = resolution self.robot_radius = robot_radius self.calc_obstacle_map(ox, oy) self.motion = self.get_motion_model() class node: def __init__(self, x, y, cost, parent_index): self.x = x # index of grid self.y = y # index of grid self.cost = cost self.parent_index = parent_index # index of previous Node def __str__(self): return str(self.x) + "," + str(self.y) + "," + str( self.cost) + "," + str(self.parent_index) def planning(self, sx, sy, gx, gy): """ dijkstra path search input: s_x: start x position [m] s_y: start y position [m] gx: Goal x position [m] gx: goal x position [m] output: rx: x position list of the final path ry: y position list of the final path """ start_node = self.Node(self.calc_xy_index(sx, self.min_x), self.calc_xy_index(sy, self.min_y), 0.0, -1) goal_node = self.Node(self.calc_xy_index(gx, self.min_x), self.calc_xy_index(gy, self.min_y), 0.0, -1) open_set, closed_set = dict(), dict() open_set[self.calc_index(start_node)] = start_node while 1: c_id = min(open_set, key=lambda o: open_set[o].cost) current = open_set[c_id] # show graph if show_animation: # pragma: no cover plt.plot(self.calc_position(current.x, self.min_x), self.calc_position(current.y, self.min_y), "xc") # for stopping simulation with the esc key. plt.GCf().canvas.mpl_connect( 'key_release_event', lambda event: [exit(0) if event.key == 'escape' else None]) if len(closed_set.keys()) % 10 == 0: plt.pause(0.001) if current.x == goal_node.x and current.y == goal_node.y: print("Find goal") goal_node.parent_index = current.parent_index goal_node.cost = current.cost break # Remove the item from the open set del open_set[c_id] # Add it to the closed set closed_set[c_id] = current # expand search grid based on motion model for move_x, move_y, move_cost in self.motion: node = self.Node(current.x + move_x, current.y + move_y, current.cost + move_cost, c_id) n_id = self.calc_index(node) if n_id in closed_set: continue if not self.verify_node(node): continue if n_id not in open_set: open_set[n_id] = node # Discover a new node else: if open_set[n_id].cost >= node.cost: # This path is the best until now. record it! open_set[n_id] = node rx, ry = self.calc_final_path(goal_node, closed_set) return rx, ry def calc_final_path(self, goal_node, closed_set): # generate final course rx, ry = [self.calc_position(goal_node.x, self.min_x)], [ self.calc_position(goal_node.y, self.min_y)] parent_index = goal_node.parent_index while parent_index != -1: n = closed_set[parent_index] rx.append(self.calc_position(n.x, self.min_x)) ry.append(self.calc_position(n.y, self.min_y)) parent_index = n.parent_index return rx, ry def calc_position(self, index, minp): pos = index * self.resolution + minp return pos def calc_xy_index(self, position, minp): return round((position - minp) / self.resolution) def calc_index(self, node): return (node.y - self.min_y) * self.x_width + (node.x - self.min_x) def verify_node(self, node): px = self.calc_position(node.x, self.min_x) py = self.calc_position(node.y, self.min_y) if px < self.min_x: return False if py < self.min_y: return False if px >= self.max_x: return False if py >= self.max_y: return False if self.obstacle_map[node.x][node.y]: return False return True def calc_obstacle_map(self, ox, oy): self.min_x = round(min(ox)) self.min_y = round(min(oy)) self.max_x = round(max(ox)) self.max_y = round(max(oy)) print("min_x:", self.min_x) print("min_y:", self.min_y) print("max_x:", self.max_x) print("max_y:", self.max_y) self.x_width = round((self.max_x - self.min_x) / self.resolution) self.y_width = round((self.max_y - self.min_y) / self.resolution) print("x_width:", self.x_width) print("y_width:", self.y_width) # obstacle map generation self.obstacle_map = [[False for _ in range(self.y_width)] for _ in range(self.x_width)] for ix in range(self.x_width): x = self.calc_position(ix, self.min_x) for iy in range(self.y_width): y = self.calc_position(iy, self.min_y) for iox, ioy in zip(ox, oy): d = math.hypot(iox - x, ioy - y) if d <= self.robot_radius: self.obstacle_map[ix][iy] = True break @staticmethod def get_motion_model(): # dx, dy, cost motion = [[1, 0, 1], [0, 1, 1], [-1, 0, 1], [0, -1, 1], [-1, -1, math.sqrt(2)], [-1, 1, math.sqrt(2)], [1, -1, math.sqrt(2)], [1, 1, math.sqrt(2)]] return motiondef main(): print(__file__ + " start!!") # start and goal position sx = -5.0 # [m] sy = -5.0 # [m] gx = 50.0 # [m] gy = 50.0 # [m] grid_size = 2.0 # [m] robot_radius = 1.0 # [m] # set obstacle positions ox, oy = [], [] for i in range(-10, 60): ox.append(i) oy.append(-10.0) for i in range(-10, 60): ox.append(60.0) oy.append(i) for i in range(-10, 61): ox.append(i) oy.append(60.0) for i in range(-10, 61): ox.append(-10.0) oy.append(i) for i in range(-10, 40): ox.append(20.0) oy.append(i) for i in range(0, 40): ox.append(40.0) oy.append(60.0 - i) if show_animation: # pragma: no cover plt.plot(ox, oy, ".k") plt.plot(sx, sy, "og") plt.plot(gx, gy, "xb") plt.grid(True) plt.axis("equal") dijkstra = Dijkstra(ox, oy, grid_size, robot_radius) rx, ry = dijkstra.planning(sx, sy, gx, gy) if show_animation: # pragma: no cover plt.plot(rx, ry, "-r") plt.pause(0.01) plt.show()if __name__ == '__main__': main()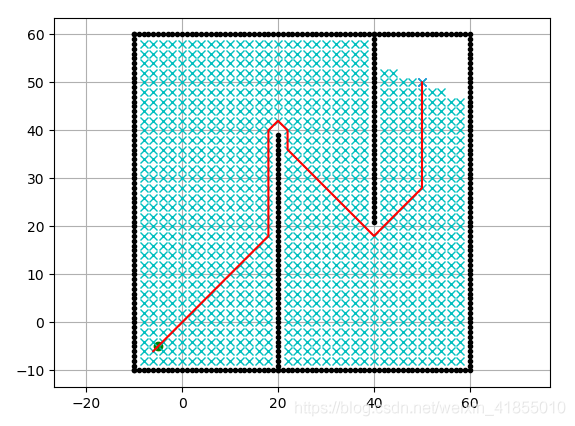
Dijkstra算法实际上是贪心搜索算法,算法复杂度为O( n 2 n^2 n2),为了减少无效搜索的次数,我们可以增加一个启发式函数(heuristic),比如搜索点到终点目标的距离,在选择open_set元素的时候,我们将cost变成cost+heuristic,就可以给出搜索的方向性,这样就可以减少南辕北辙的情况。我们可以run一下PythonRobotics中的Astar代码,得到以下结果:
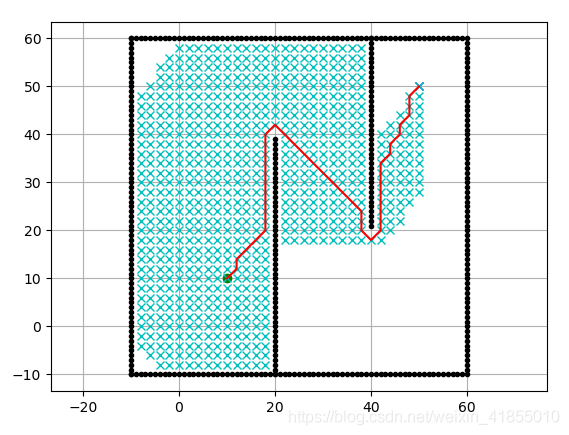
看完上述内容,你们对python中怎么利用Dijkstra算法规划机器人路径有进一步的了解吗?如果还想了解更多知识或者相关内容,请关注编程网Python频道,感谢大家的支持。
--结束END--
本文标题: python中怎么利用Dijkstra算法规划机器人路径
本文链接: https://www.lsjlt.com/news/299627.html(转载时请注明来源链接)
有问题或投稿请发送至: 邮箱/279061341@qq.com QQ/279061341
下载Word文档到电脑,方便收藏和打印~
2024-03-01
2024-03-01
2024-03-01
2024-02-29
2024-02-29
2024-02-29
2024-02-29
2024-02-29
2024-02-29
2024-02-29
回答
回答
回答
回答
回答
回答
回答
回答
回答
回答
0