Python 官方文档:入门教程 => 点击学习
使用说明 torch.cdist的使用介绍如官网所示, 它是批量计算两个向量集合的距离。 其中, x1和x2是输入的两个向量集合。 p 默认为2,为欧几里德距离。 它的功能上等同于 scipy.sp
torch.cdist的使用介绍如官网所示,
它是批量计算两个向量集合的距离。
其中, x1和x2是输入的两个向量集合。
p 默认为2,为欧几里德距离。
它的功能上等同于 scipy.spatial.distance.cdist(input,’minkowski’, p=p)
如果x1的shape是 [B,P,M], x2的shape是[B,R,M],则cdist的结果shape是 [B,P,R]
x1一般是输入矢量,而x2一般是码本。
x2中所有的元素分别与x1中的每一个元素求欧几里德距离(当p默认为2时)
如下面示例
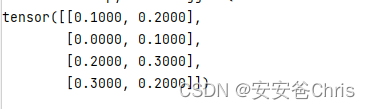
import torchx1 = torch.FloatTensor([0.1, 0.2, 0, 0.5]).view(4, 1)x2 = torch.FloatTensor([0.2, 0.3]).view(2, 1)print(torch.cdist(x1,x2))x2中的所有元素分别与x1中的每一个元素求欧几里德距离,即有如下步骤
x 11 = ( 0.1 − 0.2 ) 2 =0.1 x 12 = ( 0.1 − 0.3 ) 2 =0.2 x 21 = ( 0.2 − 0.2 ) 2 =0 x 22 = ( 0.2 − 0.3 ) 2 =0.1 x 31 = ( 0 − 0.2 ) 2 =0.2 x 32 = ( 0 − 0.3 ) 2 =0.3 x 41 = ( 0.5 − 0.2 ) 2 =0.3 x 42 = ( 0.5 − 0.3 ) 2 =0.2 x_{11} = \sqrt{ (0.1-0.2)^2} = 0.1 \newline x_{12} = \sqrt { (0.1-0.3)^2} = 0.2 \newline x_{21} = \sqrt { (0.2-0.2)^2} = 0 \newline x_{22} = \sqrt { (0.2-0.3)^2} = 0.1 \newline x_{31} = \sqrt { (0-0.2)^2} = 0.2 \newline x_{32} = \sqrt { (0-0.3)^2} = 0.3 \newline x_{41} = \sqrt { (0.5-0.2)^2 } =0.3\newline x_{42} = \sqrt { (0.5-0.3)^2 } = 0.2\newline x11=(0.1−0.2)2=0.1x12=(0.1−0.3)2=0.2x21=(0.2−0.2)2=0x22=(0.2−0.3)2=0.1x31=(0−0.2)2=0.2x32=(0−0.3)2=0.3x41=(0.5−0.2)2=0.3x42=(0.5−0.3)2=0.2
所以运行结果为
如下面示例
import torchx1 = torch.FloatTensor([0.1, 0.2, 0.1, 0.5, 0.2, -0.9, 0.8, 0.4]).view(4, 2)x2 = torch.FloatTensor([0.2, 0.3, 0, 0.1]).view(2, 2)print(torch.cdist(x1,x2))x1和x2数据是二维的,

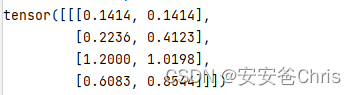
x2中的所有元素分别与x1中的每一个元素求欧几里德距离,即有如下步骤
x 11 = ( 0.1 − 0.2 ) 2 + ( 0.2 − 0.3 ) 2 = 0.02 =0.1414 x 12 = ( 0.1 − 0.0 ) 2 + ( 0.2 − 0.1 ) 2 = 0.02 =0.1414 x 21 = ( 0.1 − 0.2 ) 2 + ( 0.5 − 0.3 ) 2 = 0.05 =0.2236 x 22 = ( 0.1 − 0.0 ) 2 + ( 0.5 − 0.1 ) 2 = 0.17 =0.4123 x 31 = ( 0.2 − 0.2 ) 2 + ( − 0.9 − 0.3 ) 2 =1.2 x 32 = ( 0.2 − 0.0 ) 2 + ( − 0.9 − 0.1 ) 2 = ( 1.04)=1.0198 x 41 = ( 0.8 − 0.2 ) 2 + ( 0.4 − 0.3 ) 2 = ( 0.37)=0.6083 x 42 = ( 0.8 − 0.0 ) 2 + ( 0.4 − 0.1 ) 2 = ( 0.73)=0.8544 x_{11} = \sqrt{ (0.1-0.2)^2 + (0.2-0.3)^2 } = \sqrt{0.02} = 0.1414 \newline x_{12} = \sqrt { (0.1-0.0)^2 + (0.2-0.1)^2 } = \sqrt{0.02} = 0.1414 \newline x_{21} = \sqrt { (0.1-0.2)^2 + (0.5-0.3)^2 } = \sqrt{0.05} = 0.2236 \newline x_{22} = \sqrt { (0.1-0.0)^2 + (0.5-0.1)^2 } = \sqrt{0.17} = 0.4123 \newline x_{31} = \sqrt { (0.2-0.2)^2 + (-0.9-0.3)^2} = 1.2 \newline x_{32} = \sqrt { (0.2-0.0)^2 + (-0.9-0.1)^2} = \sqrt(1.04) = 1.0198 \newline x_{41} = \sqrt { (0.8-0.2)^2 + (0.4-0.3)^2 } = \sqrt(0.37) = 0.6083 \newline x_{42} = \sqrt { (0.8-0.0)^2 + (0.4-0.1)^2 } = \sqrt(0.73) = 0.8544 \newline x11=(0.1−0.2)2+(0.2−0.3)2=0.02=0.1414x12=(0.1−0.0)2+(0.2−0.1)2=0.02=0.1414x21=(0.1−0.2)2+(0.5−0.3)2=0.05=0.2236x22=(0.1−0.0)2+(0.5−0.1)2=0.17=0.4123x31=(0.2−0.2)2+(−0.9−0.3)2=1.2x32=(0.2−0.0)2+(−0.9−0.1)2=(1.04)=1.0198x41=(0.8−0.2)2+(0.4−0.3)2=(0.37)=0.6083x42=(0.8−0.0)2+(0.4−0.1)2=(0.73)=0.8544
所以结果如下
p=2的欧几里德距离也是L2范式,如果p=1即是L1范式
上面的例子修改一下p参数
import torchx1 = torch.FloatTensor([0.1, 0.2, 0.1, 0.5, 0.2, -0.9, 0.8, 0.4]).view(4, 2)x2 = torch.FloatTensor([0.2, 0.3, 0, 0.1]).view(2, 2)print(torch.cdist(x1,x2,p=1))结果如下,这里就不一个一个运算了。

来源地址:https://blog.csdn.net/mimiduck/article/details/128886148
--结束END--
本文标题: 【pytorch】torch.cdist使用说明
本文链接: https://www.lsjlt.com/news/391036.html(转载时请注明来源链接)
有问题或投稿请发送至: 邮箱/279061341@qq.com QQ/279061341
下载Word文档到电脑,方便收藏和打印~
2024-03-01
2024-03-01
2024-03-01
2024-02-29
2024-02-29
2024-02-29
2024-02-29
2024-02-29
2024-02-29
2024-02-29
回答
回答
回答
回答
回答
回答
回答
回答
回答
回答
0