本文实例为大家分享了Android实现页面跳转的具体代码,供大家参考,具体内容如下 一. Android实现页面跳转有两种方式,一种为.MainActivity跳转;第二种是Rela
本文实例为大家分享了Android实现页面跳转的具体代码,供大家参考,具体内容如下
一. Android实现页面跳转有两种方式,一种为.MainActivity跳转;第二种是Relatelayout布局跳转,首先看第一种方式
1. MainActivity区域设置
public class MainActivity extends AppCompatActivity {
@Override
protected void onCreate(Bundle savedInstanceState) {
super.onCreate(savedInstanceState);
setContentView(R.layout.activity_main);
//获取按钮
Button button = findViewById(R.id.button);
//按钮进行监听
button.setOnClickListener(new View.OnClickListener() {
@Override
public void onClick(View v) {
//监听按钮,如果点击,就跳转
Intent intent = new Intent();
//前一个(MainActivity.this)是目前页面,后面一个是要跳转的下一个页面
intent.setClass(MainActivity.this,NextActivity.class);
startActivity(intent);
}
});
}
}2. 这是下一个页面 的设置
public class NextActivity extends AppCompatActivity {
@Override
protected void onCreate(Bundle savedInstanceState) {
super.onCreate(savedInstanceState);
//这个是获取布局文件的,这里是你下一个页面的布局文件
setContentView(R.layout.activity_next);
}
}3. 这是第一个页面的布局文件
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="utf-8"?>
<androidx.constraintlayout.widget.ConstraintLayout xmlns:android="Http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android"
xmlns:app="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res-auto"
xmlns:tools="http://schemas.android.com/tools"
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="match_parent"
tools:context=".MainActivity">
<RelativeLayout
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="match_parent">
<TextView
android:id="@+id/one"
android:layout_width="200dp"
android:layout_height="100dp"
android:text="这是第一个页面!"
android:textSize="25dp"
android:layout_centerInParent="true"
/>
<Button
android:id="@+id/button"
android:layout_width="100dp"
android:layout_height="50dp"
tools:ignore="MissinGConstraints"
android:text="跳转"
android:layout_centerHorizontal="true"
android:layout_below="@+id/one"
/>
</RelativeLayout>
</androidx.constraintlayout.widget.ConstraintLayout>4. 这是第二个页面的布局文件
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="utf-8"?>
<androidx.constraintlayout.widget.ConstraintLayout xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android"
xmlns:app="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res-auto"
xmlns:tools="http://schemas.android.com/tools"
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="match_parent"
tools:context=".MainActivity">
<TextView
android:id="@+id/two"
android:layout_width="wrap_content"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:text="这是第二个页面!"
android:textSize="25dp"
android:textColor="#663399"
app:layout_constraintBottom_toBottomOf="parent"
app:layout_constraintLeft_toLeftOf="parent"
app:layout_constraintRight_toRightOf="parent"
app:layout_constraintTop_toTopOf="parent" />
</androidx.constraintlayout.widget.ConstraintLayout>5. AndroidManifest.xml配置加上第二个页面的入口
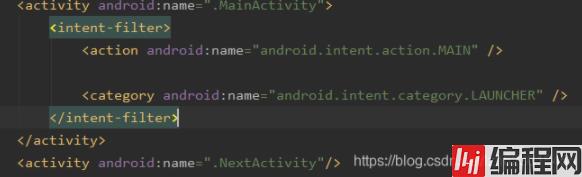
6. 效果图


二. 第二种方式是通过控制Java布局文件进行布局组合
1. 首先MainActivity文件
public class MainActivity extends AppCompatActivity {
RelativeLayout layoutTitle,layoutBox,layoutButton;
@Override
protected void onCreate(Bundle savedInstanceState) {
super.onCreate(savedInstanceState);
setContentView(R.layout.activity_main);
//获取布局文件
getwige();
}
private void getwige() {
//获取标题布局
getTitles();
//获取中间布局
getBoxs();
//获取底部布局
getButtons();
}
public void getTitles(){
//获取总布局中的标题布局
layoutTitle = this.findViewById(R.id.title);
//初始化一个标题布局类
Titles title = new Titles(this);
//进行组合布局
layoutTitle.addView(title);
}
public void getBoxs(){
//获取总布局中的中间布局
layoutBox = this.findViewById(R.id.box);
//初始化一个中间布局类
Box box = new Box(this);
//进行组合布局
layoutBox.addView(box);
}
public void getButtons(){
//获取总布局中的底部布局
layoutButton = this.findViewById(R.id.button);
//初始化一个底部布局类
Buttons buttons = new Buttons(this);
//进行组合布局
layoutButton.addView(buttons);
}
}其相对的主要布局文件如下:
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="utf-8"?>
<androidx.constraintlayout.widget.ConstraintLayout xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android"
xmlns:app="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res-auto"
xmlns:tools="http://schemas.android.com/tools"
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="match_parent"
tools:context=".MainActivity">
<RelativeLayout
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="match_parent">
<RelativeLayout
android:id="@+id/title"
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="60dp"
/>
<RelativeLayout
android:id="@+id/box"
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="590dp"
android:layout_above="@+id/button"
android:layout_below="@+id/title" />
<RelativeLayout
android:id="@+id/button"
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="80dp"
android:layout_alignParentBottom="true"
/>
</RelativeLayout>
</androidx.constraintlayout.widget.ConstraintLayout>2. 首先其他的一些组合布局的类以及其相对布局文件
1)、标题布局
public class Titles extends RelativeLayout {
public Titles(Context context) {
super(context);
View.inflate(context, R.layout.activity_title,this);
}
public Titles(Context context, AttributeSet attrs) {
super(context, attrs);
View.inflate(context, R.layout.activity_title,this);
}
public Titles(Context context, AttributeSet attrs, int defStyleAttr) {
super(context, attrs, defStyleAttr);
View.inflate(context, R.layout.activity_title,this);
}
}布局文件:
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="utf-8"?>
<androidx.constraintlayout.widget.ConstraintLayout xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android"
xmlns:app="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res-auto"
xmlns:tools="http://schemas.android.com/tools"
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="60dp"
tools:context=".MainActivity">
<RelativeLayout
android:id="@+id/title"
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="60dp"
tools:ignore="MissingConstraints"
android:background="#CCFF00">
<TextView
android:layout_width="120dp"
android:layout_height="30dp"
android:layout_centerInParent="true"
android:textSize="20dp"
android:text="这个是标题"
/>
</RelativeLayout>
</androidx.constraintlayout.widget.ConstraintLayout>2)、中间布局
public class Box extends RelativeLayout {
public Box(Context context) {
super(context);
View.inflate(context, R.layout.activity_box,this);
}
public Box(Context context, AttributeSet attrs) {
super(context, attrs);
View.inflate(context, R.layout.activity_box,this);
}
public Box(Context context, AttributeSet attrs, int defStyleAttr) {
super(context, attrs, defStyleAttr);
View.inflate(context, R.layout.activity_box,this);
}
}布局文件:
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="utf-8"?>
<androidx.constraintlayout.widget.ConstraintLayout xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android"
xmlns:app="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res-auto"
xmlns:tools="http://schemas.android.com/tools"
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="match_parent"
tools:context=".MainActivity">
<RelativeLayout
android:id="@+id/box"
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="590dp"
tools:ignore="MissingConstraints"
android:background="#6600">
<TextView
android:layout_width="150dp"
android:layout_height="590dp"
android:layout_marginTop="450dp"
android:layout_centerInParent="true"
android:textSize="20dp"
android:text="这个是中间布局"
/>
</RelativeLayout>
</androidx.constraintlayout.widget.ConstraintLayout>3)、底部布局
public class Buttons extends RelativeLayout {
public Buttons(Context context) {
super(context);
View.inflate(context, R.layout.activity_button,this);
}
public Buttons(Context context, AttributeSet attrs) {
super(context, attrs);
View.inflate(context, R.layout.activity_button,this);
}
public Buttons(Context context, AttributeSet attrs, int defStyleAttr) {
super(context, attrs, defStyleAttr);
View.inflate(context, R.layout.activity_button,this);
}
}布局文件:
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="utf-8"?>
<androidx.constraintlayout.widget.ConstraintLayout xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android"
xmlns:app="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res-auto"
xmlns:tools="http://schemas.android.com/tools"
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="match_parent"
tools:context=".MainActivity">
<RelativeLayout
android:id="@+id/box"
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="80dp"
tools:ignore="MissingConstraints"
android:background="#ccff">
<TextView
android:layout_width="150dp"
android:layout_height="30dp"
android:layout_centerInParent="true"
android:textSize="20dp"
android:text="这个是底部布局"
/>
</RelativeLayout>
</androidx.constraintlayout.widget.ConstraintLayout>效果图:

总结,其中第一中方法是真正的跳转方法,而第二中相对于一种组合布局,前者要用到两个或者多个Activity的子类,而后者只需要一个MainActivity。另外,在存在多个Activity的子类时需要设置多个入口,也就是
<activity android:name=".NextActivity"/>其中,“.”后面是你Activity的子类的名字。
--结束END--
本文标题: Android实现页面跳转
本文链接: https://www.lsjlt.com/news/151721.html(转载时请注明来源链接)
有问题或投稿请发送至: 邮箱/279061341@qq.com QQ/279061341
下载Word文档到电脑,方便收藏和打印~
2024-01-21
2023-10-28
2023-10-28
2023-10-27
2023-10-27
2023-10-27
2023-10-27
回答
回答
回答
回答
回答
回答
回答
回答
回答
回答
0