目录一、概念二、基础操作1.查找find2.插入Insert3.中序遍历InOrder4.删除erase三、递归写法1.递归查找2.递归插入3.递归删除四、应用五、题目练习一、概念
二叉搜索树又称二叉排序树,它或者是一棵空树,或者是具有以下性质的二叉树:
若它的左子树不为空,则左子树上所有节点的值都小于根节点的值
若它的右子树不为空,则右子树上所有节点的值都大于根节点的值
左<根<右
它的左右子树也分别为二叉搜索树
之所以又叫二叉排序树,是因为二叉搜索树中序遍历的结果是有序的

基于二叉搜索树的特点,查找一个数并不难,若根节点不为空的情况下:
若根节点key==查找key,直接返回true
若根节点key>查找key,那得找到更小的,则往左子树查找
若根节点key<查找key,那得找到更大的,则往右子树查找
最多查找高度次,走到空为止,如果还没找到,则说明这个值不存在,返回false
bool find(const K& key)
{
node* cur = _root;
while (cur)
{
if (cur->_key < key)
{
cur = cur->_right;
}
else if (cur->_key > key)
{
cur = cur->_left;
}
else
{
return true;
}
}
return false;
}
1.树为空,则直接插入,新增节点,直接插入root指针即可
2.树不为空,按二叉搜索树性质查找插入位置,插入新节点。
(注意:不能插入重复的元素,并且每次插入都是要定位到空节点的位置;我们先定义一个 cur从root开始,比较元素的大小:若插入的元素比当前位置元素小就往左走,比当前位置元素大就往右走,直到为空,相等就不能插入了;同时定义一个parent去记录当前 cur的前一个位置,最后判断cur是parent的左子树还是右子树即可)
bool Insert(const K& key)
{
if (_root == nullptr)
{
_root = new Node(key);
return true;
}
Node* parent = nullptr;
Node* cur = _root;
while (cur)
{
if (cur->_key < key)
{
parent = cur;
cur = cur->_right;
}
else if (cur->_key > key)
{
parent = cur;
cur = cur->_left;
}
else
{
return false;
}
}
cur = new Node(key);
if (parent->_key < key)
{
parent->_right = cur;
}
else
{
parent->_left = cur;
}
return true;
}
递归走起,同时由于_root是私有的,外部不能访问,我们可以在类内给中序提供一个方法即可,就不需要传参了
void InOrder()
{
_InOrder(_root);
cout << endl;
}
private:
void _InOrder(Node* root)
{
if (root == nullptr)
{
return;
}
_InOrder(root->_left);
cout << root->_key << " ";
_InOrder(root->_right);
}
Node* _root = nullptr;
删除的情况比较多:
但是左右都为空可以纳入到左为空或右为空的情况



注意:
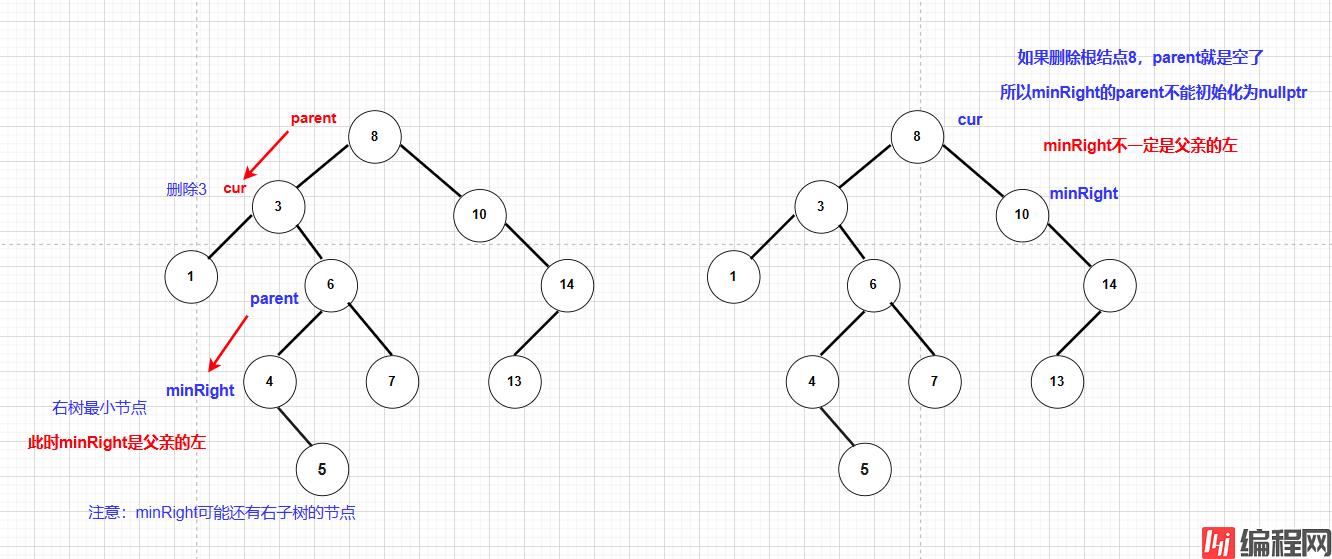
代码实现:
bool Erase(const K& key)
{
Node* parent = nullptr;
Node* cur = _root;
while (cur)
{
if (cur->_key < key)
{
parent = cur;
cur = cur->_right;
}
else if (cur->_key > key)
{
parent = cur;
cur = cur->_left;
}
else
{
//左为空
if (cur->_left == nullptr)
{
//删除根结点
//if(parent==nullptr)
if (cur == _root)
{
_root = cur->_right;
}
else
{
if (parent->_left == cur)
{
parent->_left = cur->_right;
}
else
{
parent->_right = cur->_right;
}
}
delete cur;
}
//右为空
else if (cur->_right == nullptr)
{
if (cur == _root)
{
_root = cur->_left;
}
else
{
if (parent->_left == cur)
{
parent->_left = cur->_left;
}
else
{
parent->_right = cur->_left;
}
}
delete cur;
}
//左右都不为空,找替换节点
else
{
//不能初始化为nullptr
Node* parent = cur;
//右子树最小节点
Node* minRight = cur->_right;
while (minRight->_left)
{
parent = minRight;
minRight = minRight->_left;
}
cur->_key = minRight->_key;
//判断minRight是父亲的左还是右
if (minRight == parent->_left)
{
parent->_left = minRight->_right;
}
else
{
parent->_right = minRight->_right;
}
delete minRight;
}
return true;
}
}
return false;
}
这个比较简单:苏醒把,递归时刻
bool _FindR(Node* root, const K& key)
{
if (root == nullptr) return false;
else if (root->_key < key) return _FindR(root->_right, key);
else if (root->_key > key) return _FindR(root->_left, key);
else return true;
}
最大的问题是插入之后跟父亲进行链接,如果直接给root是不可以的,因为root是栈帧里面的参数,只是局部变量:加上引用
bool _InsertR(Node*& root, const K& key)
{
if (root == nullptr)
{
root = new Node(key);
return true;
}
else if (root->_key < key)
return _InsertR(root->_right, key);
else if (root->_key > key)
return _InsertR(root->_left, key);
else
return false;
}

递归删除怎么找到父节点?root = root->_left/ root = root->_right;

bool _EraseR(Node*& root, const K& key)
{
if (root == nullptr)
{
return false;
}
if (root->_key < key)
{
return _EraseR(root->_right, key);
}
else if (root->_key > key)
{
return _EraseR(root->_left, key);
}
else
{
Node* del = root;
if (root->_right == nullptr)
{
root = root->_left;
}
else if (root->_left == nullptr)
{
root = root->_right;
}
else
{
Node* minRight = root->_right;
while (minRight->_left)
{
minRight = minRight->_left;
}
swap(root->_key, minRight->_key);
return _EraseR(root->_right, key);
}
delete del;
return true;
}
}
最优情况下,二叉搜索树为完全二叉树,其平均比较次数为:log2N
最差情况下,二叉搜索树退化为单支树,其平均比较次数为: N/2

1.K模型:K模型即只有key作为关键码,结构中只需要存储Key即可,关键码即为需要搜索到的值,判断关键字是否存在。
比如:给一个单词Word,判断该单词是否拼写正确,具体方式如下:
以单词集合中的每个单词作为key,构建一棵二叉搜索树,在二叉搜索树中检索该单词是否存在,存在则拼写正确,不存在则拼写错误。
2.KV模型:每一个关键码key,都有与之对应的值Value,即**<Key, Value>**的键值对。
比如英汉词典就是英文与中文的对应关系,通过英文可以快速找到与其对应的中文,英文单词与其对应的中文<word, chinese>就构成一种键值对;再比如统计单词次数,统计成功后,给定单词就可快速找到其出现的次数,单词与其出现次数就是**<word, count>**就构成一种键值对。
namespace KV
{
template <class K,class V>
struct BSTreeNode
{
BSTreeNode<K,V>* _left;
BSTreeNode<K,V>* _right;
K _key;
V _value;
BSTreeNode(const K& key,const V&value)
:_key(key),
_value(value),
_left(nullptr),
_right(nullptr)
{}
};
template <class K,class V>
class BSTree
{
typedef BSTreeNode<K, V> Node;
public:
bool Insert(const K& key, const V& value)
Node* find(const K& key)
void InOrder()
private:
Node* _root = nullptr;
};
}
void TestBSTree()
{
//key/Value的搜索模型;通过key查找或修改Value
KV::BSTree<string, string> dict;
dict.Insert("sort", "排序");
dict.Insert("string", "字符串");
dict.Insert("left", "左");
dict.Insert("right", "右");
string str;
while (cin >> str)
{
KV::BSTreeNode<string, string>* ret = dict.find(str);
if (ret)
{
cout << ret->_value << endl;
}
else
{
cout << "找不到" << endl;
}
}
}
源代码:
BSTree.h
#include <iOStream>
using namespace std;
namespace K
{
template <class K>
struct BSTreeNode
{
BSTreeNode<K>* _left;
BSTreeNode<K>* _right;
K _key;
BSTreeNode(const K& key)
:_key(key),
_left(nullptr),
_right(nullptr)
{}
};
template <class K>
class BSTree
{
typedef BSTreeNode<K> Node;
public:
BSTree()
:_root(nullptr)
{}
BSTree(const BSTree<K>& t)
{
_root = Copy(t._root);
}
BSTree<K>& operator = (BSTree<K> t)
{
swap(_root, t._root);
return *this;
}
~BSTree()
{
Destroy(_root);
_root = nullptr;
}
bool Insert(const K& key)
{
if (_root == nullptr)
{
_root = new Node(key);
return true;
}
Node* parent = nullptr;
Node* cur = _root;
while (cur)
{
if (cur->_key < key)
{
parent = cur;
cur = cur->_right;
}
else if (cur->_key > key)
{
parent = cur;
cur = cur->_left;
}
else
{
return false;
}
}
cur = new Node(key);
if (parent->_key < key)
{
parent->_right = cur;
}
else
{
parent->_left = cur;
}
return true;
}
bool find(const K& key)
{
Node* cur = _root;
while (cur)
{
if (cur->_key < key)
{
cur = cur->_right;
}
else if (cur->_key > key)
{
cur = cur->_left;
}
else
{
return true;
}
}
return false;
}
bool Erase(const K& key)
{
Node* parent = nullptr;
Node* cur = _root;
while (cur)
{
if (cur->_key < key)
{
parent = cur;
cur = cur->_right;
}
else if (cur->_key > key)
{
parent = cur;
cur = cur->_left;
}
else
{
//左为空
if (cur->_left == nullptr)
{
//删除根结点
//if(parent==nullptr)
if (cur == _root)
{
_root = cur->_right;
}
else
{
if (parent->_left == cur)
{
parent->_left = cur->_right;
}
else
{
parent->_right = cur->_right;
}
}
delete cur;
}
//右为空
else if (cur->_right == nullptr)
{
if (cur == _root)
{
_root = cur->_left;
}
else
{
if (parent->_left == cur)
{
parent->_left = cur->_left;
}
else
{
parent->_right = cur->_left;
}
}
delete cur;
}
//左右都不为空,找替换节点
else
{
//不能初始化为nullptr
Node* parent = cur;
//右子树最小节点
Node* minRight = cur->_right;
while (minRight->_left)
{
parent = minRight;
minRight = minRight->_left;
}
cur->_key = minRight->_key;
//判断minRight是父亲的左还是右
if (minRight == parent->_left)
{
parent->_left = minRight->_right;
}
else
{
parent->_right = minRight->_right;
}
delete minRight;
}
return true;
}
}
return false;
}
void InOrder()
{
_InOrder(_root);
cout << endl;
}
//递归
bool InsertR(const K& key)
{
return _InsertR(_root, key);
}
bool FindR(const K& key)
{
return _FindR(_root, key);
}
bool EraseR(const K& key)
{
return _EraseR(_root, key);
}
private:
void Destroy(Node* root)
{
if (root == nullptr)
{
return;
}
Destroy(root->_left);
Destroy(root->_right);
delete root;
}
Node* Copy(Node* root)
{
if (root == nullptr)
return nullptr;
Node* newRoot = new Node(root->_key);
newRoot->_left = Copy(root->_left);
newRoot->_right = Copy(root->_right);
return newRoot;
}
bool _EraseR(Node*& root, const K& key)
{
if (root == nullptr)
{
return false;
}
if (root->_key < key)
{
return _EraseR(root->_right, key);
}
else if (root->_key > key)
{
return _EraseR(root->_left, key);
}
else
{
Node* del = root;
if (root->_right == nullptr)
{
root = root->_left;
}
else if (root->_left == nullptr)
{
root = root->_right;
}
else
{
Node* minRight = root->_right;
while (minRight->_left)
{
minRight = minRight->_left;
}
swap(root->_key, minRight->_key);
return _EraseR(root->_right, key);
}
delete del;
return true;
}
}
bool _InsertR(Node*& root, const K& key)
{
if (root == nullptr)
{
root = new Node(key);
return true;
}
else if (root->_key < key)
return _InsertR(root->_right, key);
else if (root->_key > key)
return _InsertR(root->_left, key);
else
return false;
}
bool _FindR(Node* root, const K& key)
{
if (root == nullptr) return false;
else if (root->_key < key) return _FindR(root->_right, key);
else if (root->_key > key) return _FindR(root->_left, key);
else return true;
}
void _InOrder(Node* root)
{
if (root == nullptr)
{
return;
}
_InOrder(root->_left);
cout << root->_key << " ";
_InOrder(root->_right);
}
Node* _root = nullptr;
};
}
namespace KV
{
template <class K,class V>
struct BSTreeNode
{
BSTreeNode<K,V>* _left;
BSTreeNode<K,V>* _right;
K _key;
V _value;
BSTreeNode(const K& key,const V&value)
:_key(key),
_value(value),
_left(nullptr),
_right(nullptr)
{}
};
template <class K,class V>
class BSTree
{
typedef BSTreeNode<K, V> Node;
public:
bool Insert(const K& key, const V& value)
{
if (_root == nullptr)
{
_root = new Node(key, value);
return true;
}
Node* parent = nullptr;
Node* cur = _root;
while (cur)
{
if (cur->_key < key)
{
parent = cur;
cur = cur->_right;
}
else if (cur->_key > key)
{
parent = cur;
cur = cur->_left;
}
else
{
return false;
}
}
cur = new Node(key, value);
if (parent->_key < key)
{
parent->_right = cur;
}
else
{
parent->_left = cur;
}
return true;
}
Node* find(const K& key)
{
Node* cur = _root;
while (cur)
{
if (cur->_key < key)
{
cur = cur->_right;
}
else if (cur->_key > key)
{
cur = cur->_left;
}
else
{
return cur;
}
}
return nullptr;
}
void InOrder()
{
_InOrder(_root);
}
private:
void _InOrder(Node* root)
{
if (root == nullptr) return;
_InOrder(root->_left);
cout << root->_key << ":"<<root->_value<<endl;
_InOrder(root->_right);
}
Node* _root = nullptr;
};
}
void TestBSTree1()
{
int a[] = { 8, 3, 1, 10, 6, 4, 7, 14, 13 };
K::BSTree<int> t;
for (auto e : a)
{
t.Insert(e);
}
t.InOrder();
K::BSTree<int> copyt(t);
copyt.InOrder();
t.InsertR(9);
t.InOrder();
t.EraseR(9);
t.InOrder();
t.EraseR(3);
t.InOrder();
for (auto e : a)
{
t.EraseR(e);
t.InOrder();
}
}
void TestBSTree2()
{
KV::BSTree<string, string> dict;
dict.Insert("sort", "排序");
dict.Insert("string", "字符串");
dict.Insert("left", "左");
dict.Insert("right", "右");
string str;
while (cin >> str)
{
KV::BSTreeNode<string, string>* ret = dict.find(str);
if (ret)
{
cout << ret->_value << endl;
}
else
{
cout << "找不到" << endl;
}
}
}
void TestBSTree3()
{
string arr[] = { "苹果","西瓜","苹果" };
KV::BSTree<string, int> countTree;
for (auto e : arr)
{
auto* ret = countTree.find(e);
if (ret == nullptr)
{
countTree.Insert(e, 1);
}
else
{
ret->_value++;
}
}
countTree.InOrder();
}#include "BSTree.h"
int main()
{
//TestBSTree1();
TestBSTree2();
//TestBSTree3();
return 0;
}
根据二叉树创建字符串
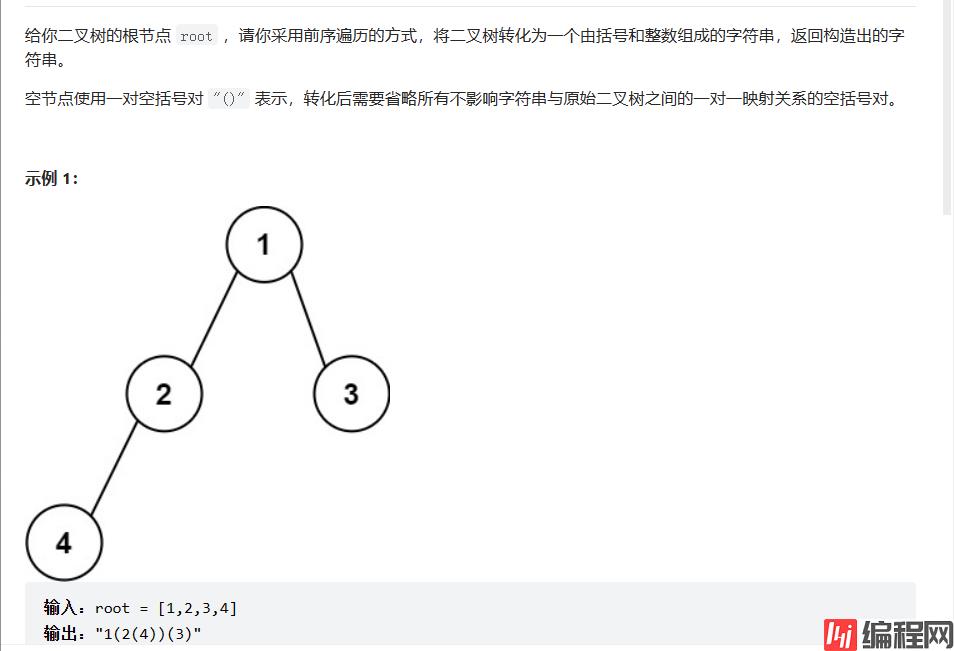
前序遍历,左为空,右不为空的括号不可以省略,右为空的括号可以省略
class Solution {
public:
string tree2str(TreeNode* root) {
if(root == nullptr) return string();
string ret;
ret += to_string(root->val);
if(root->left)
{
ret+='(';
ret+= tree2str(root->left);
ret+=')';
}
else if(root->right)
{
ret+="()";
}
if(root->right)
{
ret+='(';
ret+=tree2str(root->right);
ret+=')';
}
return ret;
}
};
二叉树的层序遍历

层序遍历,可以通过一个队列来实现,同时定义每次队列的大小
class Solution {
public:
vector<vector<int>> levelOrder(TreeNode* root) {
queue<TreeNode*> q;
vector<vector<int>> vv;
size_t levelSize = 0;
if(root)
{
q.push(root);
levelSize=1;
}
while(!q.empty())
{
vector<int> v;
while(levelSize--)
{
TreeNode* front = q.front();
q.pop();
v.push_back(front->val);
if(front->left)
{
q.push(front->left);
}
if(front->right)
{
q.push(front->right);
}
}
vv.push_back(v);
levelSize = q.size();
}
return vv;
}
};
二叉树的最近公共祖先


class Solution {
bool isInTree(TreeNode*root,TreeNode*x)
{
if(root == nullptr) return false;
if(root == x) return true;
else
return isInTree(root->left,x)
|| isInTree(root->right,x);
}
public:
TreeNode* lowestCommonAncestor(TreeNode* root, TreeNode* p, TreeNode* q) {
if(root==nullptr)
return nullptr;
if(root == p||root==q) return root;
bool pLeft = isInTree(root->left,p);
bool pRight = !pLeft;
bool qLeft = isInTree(root->left,q);
bool qRight = !qLeft;
//一个在左一个在右
if((pLeft&&qRight)||(pRight&&qLeft))
return root;
//同左
if(pLeft&&qLeft)
return lowestCommonAncestor(root->left,p,q);
//同右
else
return lowestCommonAncestor(root->right,p,q);
}
};
把根到对应节点的路径存储起来,在找出相交的结点即是最近的公共结点:

class Solution {
bool GetPath(TreeNode*root,TreeNode*x,stack<TreeNode*>& stack)
{
if(root == nullptr) return false;
stack.push(root);
if(root == x)
{
return true;
}
if(GetPath(root->left,x,stack))
return true;
if(GetPath(root->right,x,stack))
return true;
stack.pop();
return false;
}
public:
TreeNode* lowestCommonAncestor(TreeNode* root, TreeNode* p, TreeNode* q) {
if(root==nullptr)
return nullptr;
stack<TreeNode*> pPath;
stack<TreeNode*> qPath;
GetPath(root,p,pPath);
GetPath(root,q,qPath);
//长的先pop
while(pPath.size()!=qPath.size())
{
if(pPath.size()>qPath.size())
{
pPath.pop();
}
else
qPath.pop();
}
//同时pop,找出交点
while(pPath.top()!=qPath.top())
{
pPath.pop();
qPath.pop();
}
return pPath.top();
}
};
二叉搜索树与双向链表
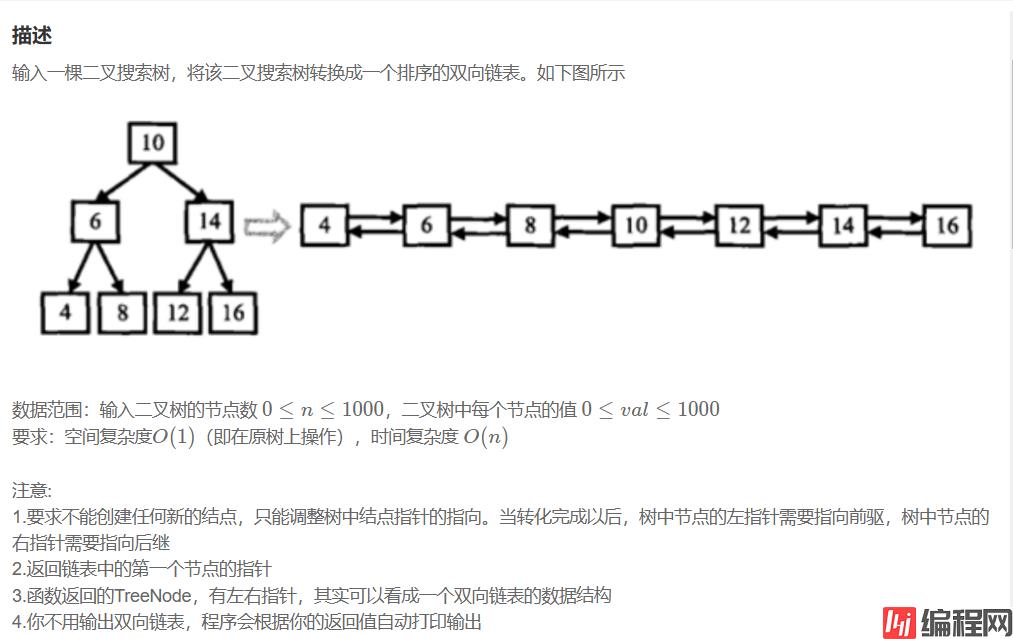
思路一:中序遍历,将节点放到一个vector中,在链接节点,但是空间复杂度不符合题目要求:
class Solution {
void InOrder(TreeNode*root,vector<TreeNode*>& v)
{
if(root==nullptr) return;
InOrder(root->left,v);
v.push_back(root);
InOrder(root->right,v);
}
public:
TreeNode* Convert(TreeNode* pRootOfTree) {
if(pRootOfTree==nullptr) return nullptr;
vector<TreeNode*> v;
InOrder(pRootOfTree,v);
if(v.size()<=1) return v[0];
v[0]->left =nullptr;
v[0]->right = v[1];
for(int i =1;i<v.size()-1;i++)
{
v[i]->left = v[i-1];
v[i]->right = v[i+1];
}
v[v.size()-1]->left = v[v.size()-2];
v[v.size()-1]->right = nullptr;
return v[0];
}
};
思路二:递归直接进行转换

class Solution {
void InOrder(TreeNode*cur,TreeNode*&prev)
{
if(cur==nullptr)
{
return;
}
InOrder(cur->left,prev);
cur->left = prev;
if(prev)
{
prev->right = cur;
}
prev = cur;
InOrder(cur->right,prev);
}
public:
TreeNode* Convert(TreeNode* pRootOfTree) {
TreeNode*prev = nullptr;
InOrder(pRootOfTree,prev);
//找头
TreeNode*head = pRootOfTree;
while(head&&head->left)
{
head = head->left;
}
return head;
}
};
从前序与中序遍历序列构造二叉树

根据前序结果去创建树,前序是根左右,前序第一个元素就是根,在通过中序去进行分割左右子树。子树区间确认是否继续递归创建子树,区间不存在则是空树。所以根据前序先构造根,在通过中序构造左子树、在构造右子树即可。
class Solution {
TreeNode* _buildTree(vector<int>& preorder, vector<int>& inorder,int&prei,int inbegin,int inend)
{
if(inbegin>inend)
{
return nullptr;
}
TreeNode*root = new TreeNode(preorder[prei]);
int rooti = inbegin;
while(inbegin<=inend)
{
if(preorder[prei] == inorder[rooti])
{
break;
}
else rooti++;
}
prei++;
//[inbegin,rooti-1]rooti[rooti+1,inend]
root->left= _buildTree(preorder,inorder,prei,inbegin,rooti-1);
root->right = _buildTree(preorder,inorder,prei,rooti+1,inend);
return root;
}
public:
TreeNode* buildTree(vector<int>& preorder, vector<int>& inorder) {
int prei = 0;
return _buildTree(preorder,inorder,prei,0,inorder.size()-1);
}
};
传引用问题:因为prei是遍历前序数组开始的下标,整个递归遍历中都要使用,所以我们需要传引用。如果不是传引用而是传值的话,左子树构建好返回,如果此时prei不是传引用,只是形参,无法将上一次递归的结果保留下来,那么也就无构建右子树了。
从中序与后序遍历序列构造二叉树

根据后序遍历的最后一个元素可以确定根结点,有了根结点做为切割点然后再去根据中序遍历划分左右区间,在继续下去,构造成二叉树,区间不存在就是空树了。同时,后序遍历是左右根,所以最后一个是根节点。所以当我们构造根结点后,由于前面是右子树,所以先构造右子树,在构造左子数。
class Solution {
TreeNode* _buildTree(vector<int>& inorder, vector<int>& postorder,int &posi,int inbegin,int inend)
{
if(inbegin>inend)
{
return nullptr;
}
TreeNode* root = new TreeNode(postorder[posi]);
int rooti = inbegin;
while(inbegin<=inend)
{
if(postorder[posi] == inorder[rooti])
{
break;
}
else rooti++;
}
posi--;
//[inbegin,rooti-1]rooti[rooti+1,inend];
root->right = _buildTree(inorder,postorder,posi,rooti+1,inend);
root->left = _buildTree(inorder,postorder,posi,inbegin,rooti-1);
return root;
}
public:
TreeNode* buildTree(vector<int>& inorder, vector<int>& postorder) {
int posi = postorder.size()-1;
return _buildTree(inorder,postorder,posi,0,inorder.size()-1);
}
};

到此这篇关于c++二叉搜索树BSTree使用详解的文章就介绍到这了,更多相关C++二叉搜索树内容请搜索编程网以前的文章或继续浏览下面的相关文章希望大家以后多多支持编程网!
--结束END--
本文标题: C++二叉搜索树BSTree使用详解
本文链接: https://www.lsjlt.com/news/199139.html(转载时请注明来源链接)
有问题或投稿请发送至: 邮箱/279061341@qq.com QQ/279061341
下载Word文档到电脑,方便收藏和打印~
2024-03-01
2024-03-01
2024-02-29
2024-02-29
2024-02-29
2024-02-29
2024-02-29
2024-02-29
2024-02-29
2024-02-29
回答
回答
回答
回答
回答
回答
回答
回答
回答
回答
0